Spring(一) IOC核心类
Spring(二) Resource定位与载入
Spring(三) BeanDefinition解析与注册
Spring(四) 自定义标签解析
Spring(五) 其他初始化步骤
Spring(六) bean的加载01
Spring(七) bean的加载02
Spring(八) SpringBean的生命周期
Spring(九) IOC时序图
Spring(十) AOP 01
Spring(十一) AOP 02
Spring(十二) spring事务
代码回顾
AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法,前3篇对BeanDefinition的生成与注册做了跟踪
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 准备工作:设置spring启动时间,是否结束/激活标识;初始化属性源(默认空方法,留给子类覆盖);验证必要属性
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 创建beanFactory,如果已有就销毁后创建,这里就是实现BeanFactory全部功能的地方,
// 过程是对BeanDefinition的装载: 根据xml为每个bean生成BeanDefinition并注册到生成的beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// c.配置创建好的beanFactory的标准上下文配置
// 给beanFactory设置ClassLoader,设置SpEL表达式解析器,设置类型转化器[能将xml String类型转成相应对象],
// 增加内置ApplicationContextAwareProcessor对象,忽略各种Aware对象,注册各种内置的对账对象[BeanFactory,ApplicationContext]等,
// 注册环境相关的一些系统属性等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// d.模板方法,提供一个修改容器的beanFactory的入口,子类特殊的bean factory设置,默认为空实现
// 比如GenericWebApplicationContext容器会在BeanFactory中添加ServletContextAwareProcessor。
// 用于处理ServletContextAware类型的bean,初始化的时候调用setServletContext或者setServletConfig方法
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// e.从Spring容器中找出BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类,实例化并按照一定的规则顺序进行执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
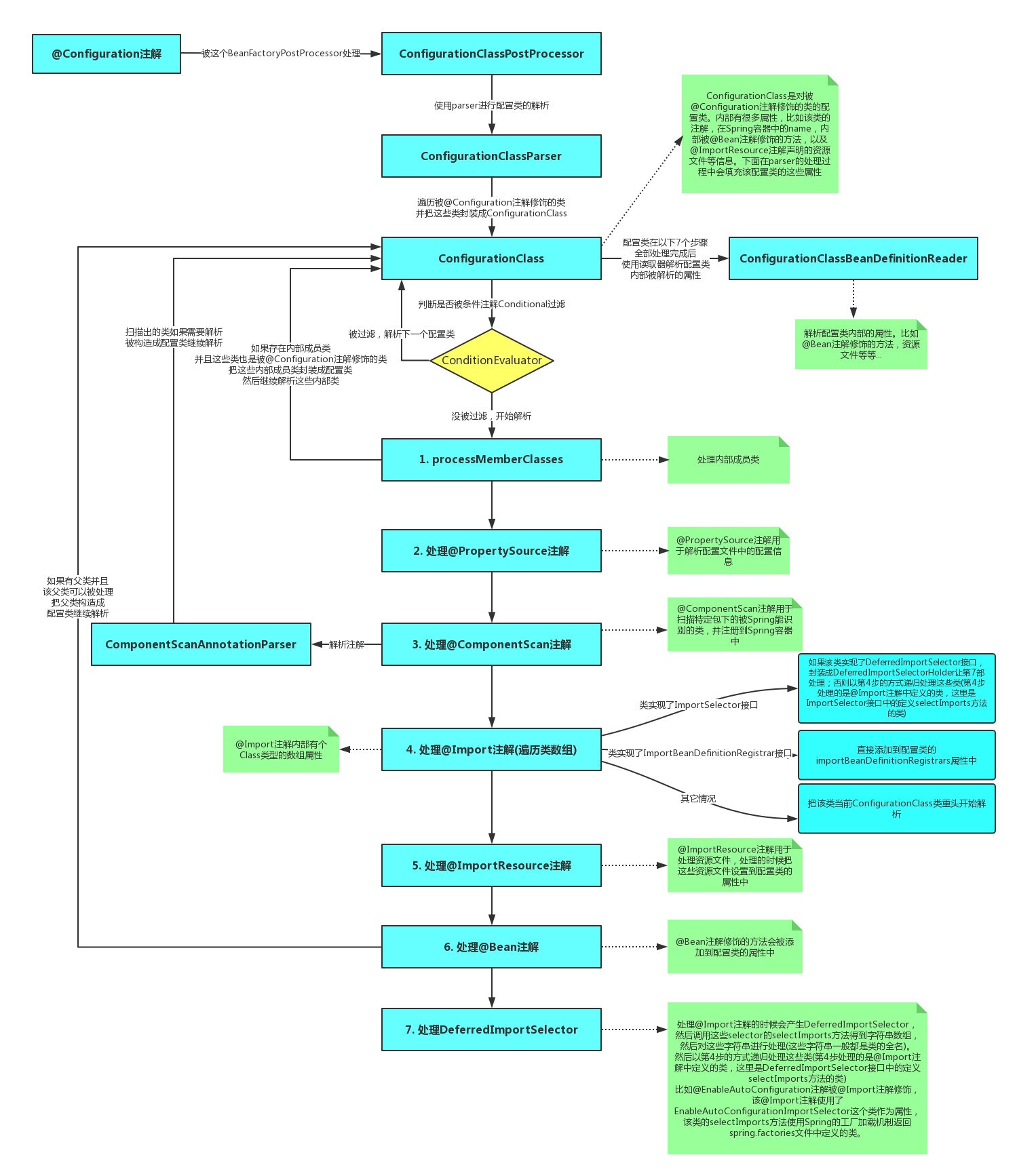
// (在用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext时会register这个)比如ConfigurationClassPostProcessor(实现了PriorityOrdered接口),会去BeanFactory中找出所有有@Configuration注解的bean,然后使用ConfigurationClassParser去解析这个类,解析完成之后把这些bean注册到BeanFactory中。需要注意的是这个时候注册进来的bean还没有实例化
// 其内部有个Map类型的configurationClasses属性用于保存解析的类,ConfigurationClass是一个对要解析的配置类的封装,内部存储了配置类的注解信息、被@Bean注解修饰的方法、@ImportResource注解修饰的信息、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar等都存储在这个封装类中(@Component、@ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource修饰的类)
// 这个processor是优先级最高的被执行的processor,另外如果程序中有自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,那么这个PostProcessor首先得通过ConfigurationClassPostProcessor被解析出来,然后才能被Spring容器找到并执行
// 比如PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,用来解析${...}占位符
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// f.实例化、注册用于拦截bean创建过程的BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// g.实例化,注册和设置国际化工具类MessageSource
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// h.实例化,注册和设置事件广播器,用于发布事件(如果没有自己定义使用默认的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster实现,此广播使用同步的通知方式)
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// i.模板方法,调用子类特殊的刷新逻辑,默认为空方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// j.为事件广播器注册事件监听器,添加ApplicationListener实现类到上面设置的事件广播器ApplicationEventMulticaster
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// k(待).完成容器的初始化,实例化BeanFactory中已经被注册但是没被实例化的所有单例(懒加载除外)
// 设置自定义的类型转化器ConversionService,设置自定义AOP相关的类LoadTimeWeaverAware,清除临时的ClassLoader,冻结配置
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// l.初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件
// 初始化生命周期处理器LifecycleProcessor(默认使用DefaultLifecycleProcessor)并调用其onrefresh方法,找到SmartLifecycle接口的所有实现类并调用start方法
// 发布事件告知listener,如果设置了JMX相关属性,还会调用LiveBeansView的registerApplicationContext方法
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
// m.重置缓存
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
c.Bean工厂准备
c-1 . 配置创建好的beanFactory的标准上下文配置
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 设置beanFactory的classLoader为当前context的classLoader
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 设置beanFactory的表达式语言处理器,spring3增加了表达式语言的支持,默认可以使用#{bean.xxx}的形式来调用相关属性值。
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
// 添加属性编辑器,更准确应该是属性转换器,比如从String到Date类型的转化
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 添加后置处理器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 忽略给定接口的自动装配功能,典型应用是通过XXAware接口进行注入时不需要自动初始化依赖属性
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 设置几个自动装配规则,例如如果是BeanFactory则注入beanFactory
// 如果是ResourceLoader,ApplicationEventPublisher,ApplicationContext注入当前对象
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
// 如果包含LoadTimeWeaver,增加对AspectJ支持
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 添加后置处理器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
// 这里个属性都是系统属性,之前是单独存在的并没有注入到容器中,这里把系统属性注入到容器中
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
e.调用beanFactoryPostProcessor
e-1 . 真正的BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行任务委托给Spring工具类PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate完成
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// getBeanFactoryPostProcessors: 获取的手动注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// 如果同时发现了一个LoadTimeWeaver就做相应的织入准备
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
e-2 . 执行它们的postProcessBeanFactory方法
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
// 处理过的bean
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
// 对BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的处理
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 硬编码注册的后处理器
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { // 子接口
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 对于BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcess类型,在BeanFactoryPostProcessor基础上还有自己定义的方法,需要先调用
// 通过AbstractApplicationContext中添加处理器方法addBeanFactoryPostProcessor进行添加
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
// 记录常规BeanFactoryPostProcessor
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
// 当前待处理BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 配置注册的后处理器(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor),PriorityOrdered、Ordered、其他
// 处理方法都相同: 放入容器,排序,执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的生命周期方法postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// PriorityOrdered实现类
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// Ordered实现类
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
// 3种类型处理完后,再执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的生命周期方法postProcessBeanFactory
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.\
// 否则直接执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的生命周期方法postProcessBeanFactory
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// 再处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor,处理的方式同上面的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor一致
// 先处理完PriorityOrdered,再处理Ordered,最后处理普通的
// 要注意的是,因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor也是BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并且他之前已经处理过了,所以这个过程就不会在处理了
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
例子:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor(图片来自互联网)
Spring内部的BeanPostProcessor接口总结
Spring内置的BeanPostProcessor总结
f.注册BeanPostProcessors
f-1 . 委托给PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate类的registerBeanPostProcessors方法执行
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
f-2 . 这里的过程跟invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors类似
比如AnnotationConfigUtils的registerAnnotationConfigProcessors方法注册的,这些BeanPostProcessor包括有AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理被@Autowired注解修饰的bean并注入)、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理被@Required注解修饰的方法)、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理@PreDestroy、@PostConstruct、@Resource等多个注解的作用)等。 如果是自定义的BeanPostProcessor,已经被ConfigurationClassPostProcessor注册到容器内。
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 注册到beanFactory中的List里
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 这些BeanPostProcessor会在这个方法内被实例化(通过调用BeanFactory的getBean方法,如果没有找到实例化的类,就会去实例化)
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
l.完成最后初始化步骤
l-1 . 完成上下文刷新,调用LifecycleProcessor的onRefresh方法并且发布ContextRefreshedEvent
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
// 清空resourceCaches缓存: resourceCaches.clear()
clearResourceCaches();
// -2:Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// -3:Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// -5:Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// -6:Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
l-2 . 初始化LifecycleProcessor
protected void initLifecycleProcessor() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.lifecycleProcessor =
beanFactory.getBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, LifecycleProcessor.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using LifecycleProcessor [" + this.lifecycleProcessor + "]");
}
}
else {
// 上下文没有找到则创建DefaultLifecycleProcessor
DefaultLifecycleProcessor defaultProcessor = new DefaultLifecycleProcessor();
defaultProcessor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.lifecycleProcessor = defaultProcessor;
// 注册,放入factory单例cache,放入manualSingletonNames
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, this.lifecycleProcessor);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate LifecycleProcessor with name '" +
LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.lifecycleProcessor + "]");
}
}
}
l-3 . 调用之前创建的DefaultLifecycleProcessor的onRefresh方法
public void onRefresh() {
startBeans(true);
this.running = true;
}
l-4 . SmartLifecycle接口的所有实现类并调用start方法
private void startBeans(boolean autoStartupOnly) {
Map<String, Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans = getLifecycleBeans();
Map<Integer, LifecycleGroup> phases = new HashMap<>();
lifecycleBeans.forEach((beanName, bean) -> {
if (!autoStartupOnly || (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle && ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
int phase = getPhase(bean);
LifecycleGroup group = phases.get(phase);
if (group == null) {
group = new LifecycleGroup(phase, this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase, lifecycleBeans, autoStartupOnly);
phases.put(phase, group);
}
group.add(beanName, bean);
}
});
if (!phases.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> keys = new ArrayList<>(phases.keySet());
Collections.sort(keys);
for (Integer key : keys) {
phases.get(key).start();
}
}
}
public void start() {
if (this.members.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Starting beans in phase " + this.phase);
}
Collections.sort(this.members);
for (LifecycleGroupMember member : this.members) {
if (this.lifecycleBeans.containsKey(member.name)) {
doStart(this.lifecycleBeans, member.name, this.autoStartupOnly);
}
}
}
private void doStart(Map<String, ? extends Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans, String beanName, boolean autoStartupOnly) {
Lifecycle bean = lifecycleBeans.remove(beanName);
if (bean != null && bean != this) {
String[] dependenciesForBean = getBeanFactory().getDependenciesForBean(beanName);
for (String dependency : dependenciesForBean) {
doStart(lifecycleBeans, dependency, autoStartupOnly);
}
if (!bean.isRunning() &&
(!autoStartupOnly || !(bean instanceof SmartLifecycle) || ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Starting bean '" + beanName + "' of type [" + bean.getClass() + "]");
}
try {
// 调用SmartLifecycle接口实现类的start方法
bean.start();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to start bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Successfully started bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
}
}
l-5 . 发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件告知对应的ApplicationListener进行响应的操作
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
}
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
// 创建的ContextRefreshedEvent是继承自ApplicationEvent
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
// 使用上注册的事件广播器ApplicationEventMulticaster(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster)广播ContextRefreshedEvent事件
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
l-6 . 调用LiveBeansView的registerApplicationContext方法
static void registerApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String mbeanDomain = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty(MBEAN_DOMAIN_PROPERTY_NAME);
// 看是否配置了spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain属性
if (mbeanDomain != null) {
synchronized (applicationContexts) {
if (applicationContexts.isEmpty()) {
try {
MBeanServer server = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
applicationName = applicationContext.getApplicationName();
server.registerMBean(new LiveBeansView(),
new ObjectName(mbeanDomain, MBEAN_APPLICATION_KEY, applicationName));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to register LiveBeansView MBean", ex);
}
}
applicationContexts.add(applicationContext);
}
}
}
m.重置缓存
// Reset Spring's common reflection metadata caches
protected void resetCommonCaches() {
ReflectionUtils.clearCache();
AnnotationUtils.clearCache();
ResolvableType.clearCache();
CachedIntrospectionResults.clearClassLoader(getClassLoader());
}