Spring(一) IOC核心类
Spring(二) Resource定位与载入
Spring(三) BeanDefinition解析与注册
Spring(四) 自定义标签解析
Spring(五) 其他初始化步骤
Spring(六) bean的加载01
Spring(七) bean的加载02
Spring(八) SpringBean的生命周期
Spring(九) IOC时序图
Spring(十) AOP 01
Spring(十一) AOP 02
Spring(十二) spring事务
AOP概念
- 横切关注点: 对哪些方法进行拦截,拦截后怎么处理,这些关注点称之为横切关注点
- 切面(aspect): 切面就是对横切关注点的抽象
- 连接点(joinpoint): 被拦截到的点,因为Spring只支持方法类型的连接点,所以在Spring中连接点指的就是被拦截到的方法,实际上连接点还可以是字段或者构造器
- 切入点(pointcut): 对连接点进行拦截的定义
- 目标对象: 代理的目标对象
- 通知(advice): 指拦截到连接点之后要执行的代码,通知分为前置、后置、异常、最终、环绕通知五类
- Advisor: 是Pointcut和Advice的配置器,它包括Pointcut和Advice,是将Advice注入程序中Pointcut位置的代码
- 织入(weave): 将切面应用到目标对象并创建代理对象的过程
- 引入(introduction): 在不修改代码的前提下,引入可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或字段
JDK中的动态代理
- 创建InvocationHandler接口实现类(代理执行类),创建构造函数传入被代理对象
- 实现invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)方法,实现AOP增强逻辑
- 创建getProxy方法,也可以在外面直接调用代码
- Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), this)
- 创建目标被代理类与接口
- 实例化InvocationHandler实现类,传入接口,getProxy方法获得代理对象,调用代理对象方法
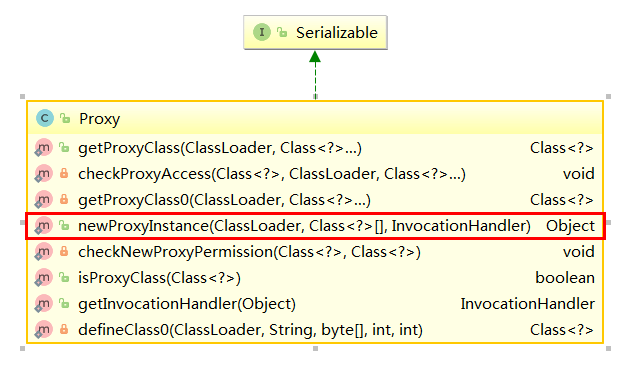
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, // 用于加载代理类的 Loader 类,通常这个 Loader 和被代理的类是同一个 Loader 类
Class<?>[] interfaces, // 要被代理的那些那些接口
InvocationHandler h) // 用于执行除了被代理接口中方法之外的用户自定义的操作
throws IllegalArgumentException {
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
// 拷贝接口数组对象
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
// 查找或生成指定的代理类
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
* 调用指定的调用处理程序的构造函数
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
// 校验新代理类的权限
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
// 获取代理类构造函数,参数类型必须为InvocationHandler
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
// 构造函数不是public,则设置当前构造函数为访问权限
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
// 生成代理类的实例并把InvocationHandler的实例传给它的构造方法
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>... interfaces) {
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
}
// If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing
// the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy;
// otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
}
// proxyClassCache定义
private static final WeakCache<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
proxyClassCache = new WeakCache<>(new KeyFactory(), new ProxyClassFactory());
// 拿到代理类
public V get(K key, P parameter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(parameter);
expungeStaleEntries();
Object cacheKey = CacheKey.valueOf(key, refQueue);
// lazily install the 2nd level valuesMap for the particular cacheKey
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap = map.get(cacheKey);
if (valuesMap == null) {
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> oldValuesMap
= map.putIfAbsent(cacheKey,
valuesMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
if (oldValuesMap != null) {
valuesMap = oldValuesMap;
}
}
// create subKey and retrieve the possible Supplier<V> stored by that
// subKey from valuesMap
Object subKey = Objects.requireNonNull(subKeyFactory.apply(key, parameter));
Supplier<V> supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
Factory factory = null;
while (true) {
if (supplier != null) {
// supplier might be a Factory or a CacheValue<V> instance
V value = supplier.get();
if (value != null) {
// 这里返回,所以是从supplier中生成了代理类
return value;
}
}
// else no supplier in cache
// or a supplier that returned null (could be a cleared CacheValue
// or a Factory that wasn't successful in installing the CacheValue)
// lazily construct a Factory
if (factory == null) {
factory = new Factory(key, parameter, subKey, valuesMap);
}
if (supplier == null) {
supplier = valuesMap.putIfAbsent(subKey, factory);
if (supplier == null) {
// successfully installed Factory
supplier = factory;
}
// else retry with winning supplier
} else {
if (valuesMap.replace(subKey, supplier, factory)) {
// successfully replaced
// cleared CacheEntry / unsuccessful Factory
// with our Factory
supplier = factory;
} else {
// retry with current supplier
supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
}
}
}
}
Spring对AOP的支持
Spring中AOP代理由Spring的IOC容器负责生成、管理,其依赖关系也由IOC容器负责管理。因此,AOP代理可以直接使用容器中的其它bean实例作为目标,这种关系可由IOC容器的依赖注入提供。Spring创建代理的规则为:
1、默认使用Java动态代理来创建AOP代理,这样就可以为任何接口实例创建代理了
2、当需要代理的类不是代理接口的时候,Spring会切换为使用CGLIB代理,也可强制使用CGLIB
applicationContext配置方式:
1、”aop:config” + “aop:aspect” + “aop:pointcut + aop:before/aop:after/aop:around…”
2、”aop:aspectj-autoproxy” + “@Aspect + @Pointcut + @Before/@After/@Around…”
3、”aop:config” + “aop:advisor” + “MethodBeforeAdvice接口实现类/AfterReturningAdvice接口实现类/MethodInterceptor接口实现类…”
spring advice执行顺序:
单个内部:
正常:@Around -> @Before -> invoke -> @Around -> @After -> @AfterReturning
异常:@Around -> @Before -> invoke -> @After -> @AfterThrowing
多个之间:
按order大小排序包裹: [order:1 [order:2 [method] order:2] order:1]
注:advice方法里可以拿到JoinPoint接口的实现类,@AfterThrowing另外还可以拿到Throwable
源码分析
parseCustomElement
自定义标签解析,根据命名空间找到NamespaceHandler,即AopNamespaceHandler,在其resolve方法中调用init初始化注册
public void init() {
// In 2.0 XSD as well as in 2.1 XSD.
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config", new ConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("aspectj-autoproxy", new AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionDecorator("scoped-proxy", new ScopedProxyBeanDefinitionDecorator());
// Only in 2.0 XSD: moved to context namespace as of 2.1
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
}
config标签
注册了ConfigBeanDefinitionParser(BeanDefinitionParser接口实现类)后,对于config类型标签,parseCustomElement方法调用其parse方法
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef =
new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), parserContext.extractSource(element));
parserContext.pushContainingComponent(compositeDef);
// AopNamespaceUtils.registerAspectJAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element)
// 注册AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
configureAutoProxyCreator(parserContext, element);
// 子元素处理
List<Element> childElts = DomUtils.getChildElements(element);
for (Element elt: childElts) {
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(elt);
// pointcut处理
if (POINTCUT.equals(localName)) {
parsePointcut(elt, parserContext);
}
// advisor处理
else if (ADVISOR.equals(localName)) {
parseAdvisor(elt, parserContext);
}
// aspect处理
else if (ASPECT.equals(localName)) {
parseAspect(elt, parserContext);
}
}
parserContext.popAndRegisterContainingComponent();
return null;
}
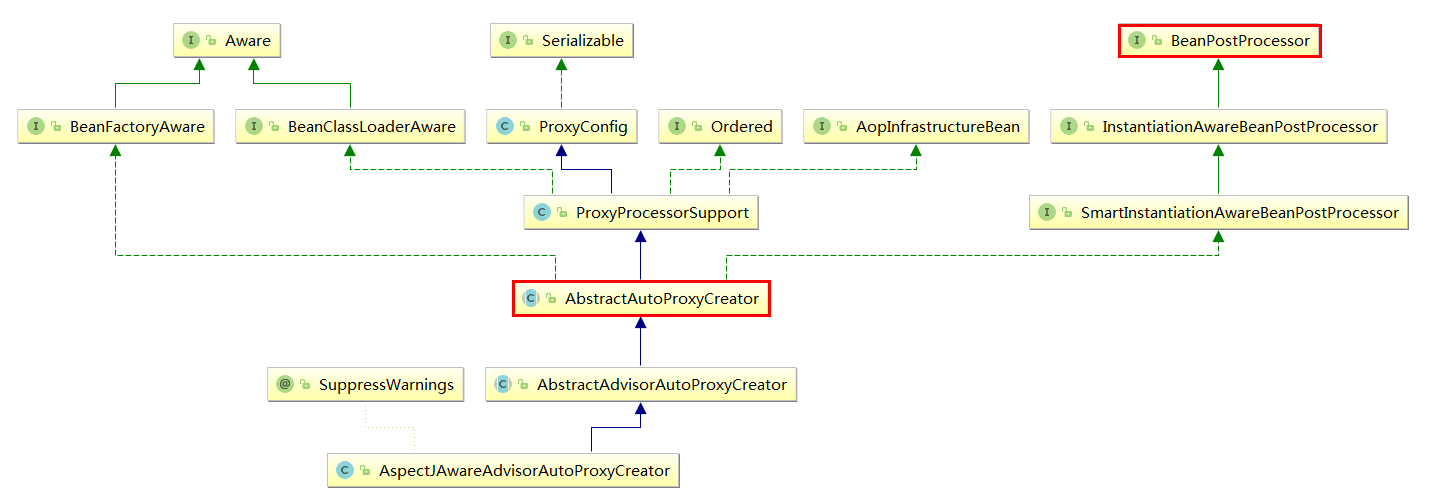
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,会被调用其postProcessAfterInitialization方法,然后调用其父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator的wrapIfNecessary方法
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
aspectj-autoproxy标签
对于<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />标签
parse
注册了AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser(BeanDefinitionParser接口实现类)后,parseCustomElement方法同样调用其parse方法
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
AopNamespaceUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(parserContext, element);
// 对注解中子类的处理
extendBeanDefinition(element, parserContext);
return null;
}
1 . 注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
public static void registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
ParserContext parserContext, Element sourceElement) {
// a. 注册或升级AutoProxyCreator定义beanName为internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(
parserContext.getRegistry(), parserContext.extractSource(sourceElement));
// b. 对proxy-target-class与expose-proxy属性的处理
useClassProxyingIfNecessary(parserContext.getRegistry(), sourceElement);
// 注册组件并通知,便于监听器做进一步处理
registerComponentIfNecessary(beanDefinition, parserContext);
}
1-a . 对于AOP的实现,基本是靠AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator去完成,它可以根据@Point注解定义的切点来自动代理相匹配的bean。但是为了配置方便,Spring使用了自定义配置来帮助自动注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
// AopConfigUtils
public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
// 如果已经存在了自动代理创建器并且存在的与现在的不一致,则需要根据优先级判断使用哪一个
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
// 改变bean最重要的就是改变bean所对应的className属性
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
// 如果已经存在了自动代理创建器并且一致,那就不需再创建了
return null;
}
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
// order为最小值,优先级最大
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
1-b . 处理proxy-target-class与expose-proxy属性
private static void useClassProxyingIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Element sourceElement) {
if (sourceElement != null) {
boolean proxyTargetClass = Boolean.parseBoolean(sourceElement.getAttribute(PROXY_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE));
if (proxyTargetClass) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
boolean exposeProxy = Boolean.parseBoolean(sourceElement.getAttribute(EXPOSE_PROXY_ATTRIBUTE));
if (exposeProxy) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
// 强制使用的过程,其实就是个属性设置的过程
// proxy-target-class设为true来强制使用CGLIB代理
// JDK动态代理,其代理对象必须是某个接口的实现,它是通过在运行期间创建一个接口的实现类来完成对目标对象的代理
// CGLIB代理,实现原理类似,但是是在运行期间生成的对象是针对目标类扩展的子类。底层依靠ASM(字节码编辑类库)操作字节码实现的,性能更好
public static void forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition definition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.TRUE);
}
}
// expose-proxy设为true来让目标对象内部的自我调用(this.xx)得到切面增强处理
public static void forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition definition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("exposeProxy", Boolean.TRUE);
}
}
2 . 注解中子类的处理
private void extendBeanDefinition(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
BeanDefinition beanDef =
parserContext.getRegistry().getBeanDefinition(AopConfigUtils.AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (element.hasChildNodes()) {
addIncludePatterns(element, parserContext, beanDef);
}
}
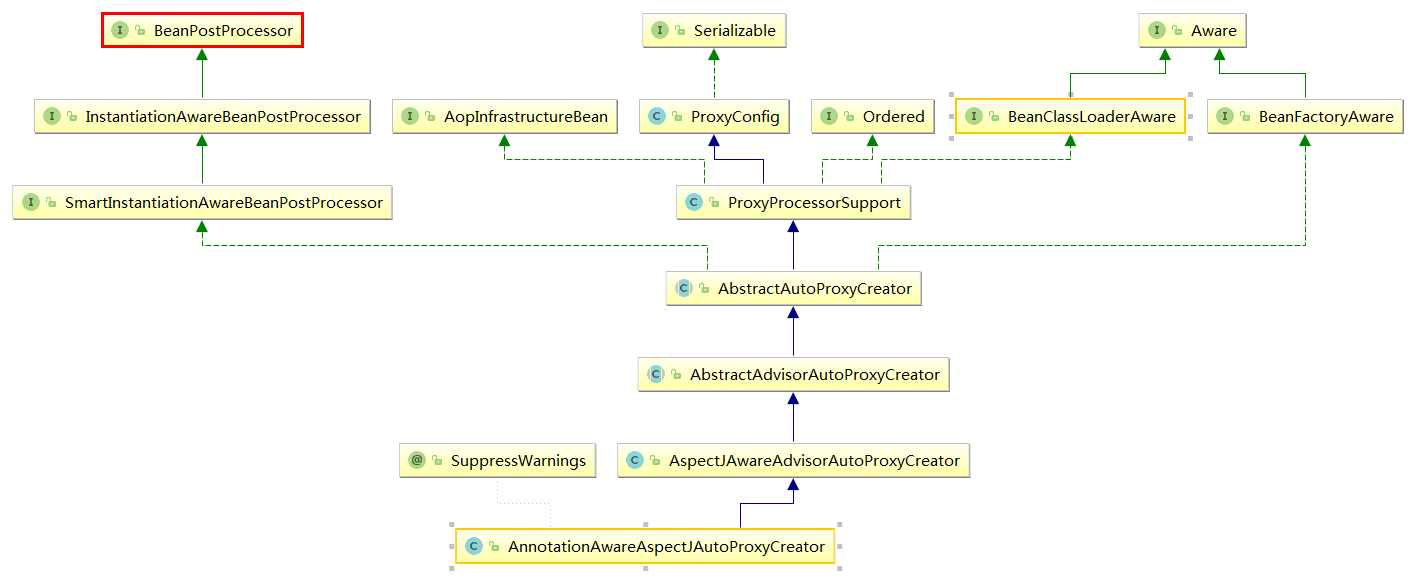
postProcessAfterInitialization
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator也实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,所以当Spring预实例化bean后会调用其postProcessAfterInitialization方法
// AbstractAutoProxyCreator
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
// 根据给定的beanClass和beanName构建出Key
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
// 如果它需要被代理,则封装指定的bean
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
1 . 创建aop代理
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 如果已被处理过,返回
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
// 不需要增强
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
// 是一个基础设施类 或 配置的指定bean不需要自动代理
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 如果有增强方法,则创建代理 Create proxy if we have advice.
// a. 获取增强方法
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 如果获取到了增强则需要针对增强创建代理
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// b. 创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
1-a . 获取增强方法或增强器
// AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 1. 获取增强器
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 2. 获取其中能应用(合适)的增强器
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
1-a-1 . 获取增强器
// AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
// 当使用注解方式配置aop时,也会获取XML的配置,这里调用父类方法加载配置文件中的AOP声明
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
// 添加bean注解增强
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}
1-a-2 . 获取注解增强
在实例化单例的时候,会调用resolveBeforeInstantiation方法(Spring(七)b.实例化的前置处理),里面会调用applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation方法,获取到org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator(也是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口实现类),调用它的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法。在判断shouldSkip时,会去findCandidateAdvisors,那时候会调用buildAspectJAdvisors方法,所以在缓存中已经能取到aspectNames和cachedAdvisors了
// BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
// AspectJ注解类
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取所有beanName
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
// 遍历找出对应的增强类
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 不合法bean跳过,由子类定义规则,默认返回false
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
// 获取对应bean类型
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 如果存在AspectJ注解
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// ----> 解析标记AspectJ注解中的增强方法
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
// ----> 加入解析标记AspectJ注解中的增强方法
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 记录到缓存中
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
// ---->
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
1-a-3 . getAdvisors解析获取
// ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
// 获取标记为AspectJ的类与名字,然后做验证
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// ----> 1. 获取增强器
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
// 2. 如果寻找的增强器不为空,并且配置了增强延迟初始化,那么需要在首位0加入同步实例化增强器
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
// 3. 获取DeclareParents注解
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
}
1-a-4 . getAdvisor获取增强器
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
// ----> 获取切入点信息
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
// ----> 根据切入点生成增强器
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
1-a-5 . 获取切入点信息
private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class<?> candidateAspectClass) {
// ----> 获取方法上的注解
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// 使用AspectJExpressionPointcut实例封装获取的信息
AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =
new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class<?>[0]);
// 提取得到的注解中的表达式 execution(* *.*..*(..))
ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression());
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
ajexp.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
return ajexp;
}
1-a-6 . 获取方法上的注解
// AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory
protected static AspectJAnnotation<?> findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(Method method) {
// 设置查找的注解classes
Class<?>[] classesToLookFor = new Class<?>[] {
Before.class, Around.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class, Pointcut.class};
for (Class<?> c : classesToLookFor) {
AspectJAnnotation<?> foundAnnotation = findAnnotation(method, (Class<Annotation>) c);
if (foundAnnotation != null) {
return foundAnnotation;
}
}
return null;
}
1-a-7 . 根据切入点生成增强器
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut;
this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass();
this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName();
this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes();
this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod;
this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory;
this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory;
this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder;
this.aspectName = aspectName;
if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
// Static part of the pointcut is a lazy type.
Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union(
aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this.declaredPointcut);
// Make it dynamic: must mutate from pre-instantiation to post-instantiation state.
// If it's not a dynamic pointcut, it may be optimized out
// by the Spring AOP infrastructure after the first evaluation.
this.pointcut = new PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut(
this.declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
this.lazy = true;
}
else {
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
// ----> 不同的增强逻辑是不同的,需要完成不同的逻辑
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
}
}
1-a-8 . 初始化不同的增强器
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {
Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);
}
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
// 根据不同的注解类型封装不同的增强器
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtBefore:
// 拦截器内放置MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor中放置AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
// 直接在拦截器链中使用AspectJAfterAdvice
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
1-a-9 . 回到1-a-3,如果寻找的增强器不为空,并且又配置了增强延迟初始化,那就要在首位加入同步实例增强器
protected static class SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor extends DefaultPointcutAdvisor {
public SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(final MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aif) {
// 目标方法前调用,类似@before
super(aif.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), (MethodBeforeAdvice)
// 简单初始化aspect
(method, args, target) -> aif.getAspectInstance());
}
}
1-a-10 . 回到1-a-3,获取DeclareParents注解,DeclareParents主要用于引介增强(对类级别的增强,可以通过引介增强为目标类添加新的属性和方法,这些新属性或方法是可以根据我们业务逻辑需求而动态变化的)的注解形式的实现,其实现方式和普通增强类似,只不过使用DeclareParentsAdvisor对功能进行封装
private Advisor getDeclareParentsAdvisor(Field introductionField) {
DeclareParents declareParents = introductionField.getAnnotation(DeclareParents.class);
if (declareParents == null) {
// Not an introduction field
return null;
}
if (DeclareParents.class == declareParents.defaultImpl()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("'defaultImpl' attribute must be set on DeclareParents");
}
return new DeclareParentsAdvisor(
introductionField.getType(), declareParents.value(), declareParents.defaultImpl());
}
1-a-11 . 回到1-a,获取其中能应用(合适)的增强器
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
// ----> 过滤Advisors
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 首先处理引介增强
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 引介增强已处理,跳过
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
// 对普通增强处理
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
1-a-12 . 判断是否匹配
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));
}
classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
这样就返回Advisor的数组,然后去创建代理