Dubbo(一):从dubbo-demo初探dubbo源码
Dubbo(二):架构与SPI
Dubbo(三):高并发下降级与限流
Dubbo(四):其他常用特性
Dubbo(五):自定义扩展
准备工作
源码从github上clone,本文源码2.6.1,查看服务调用时升到了2.7.0,目前看区别就netty版本的不同导致发送请求时调用不一样。
使用zookeeper作为注册中心,从官网下载
通过maven构建项目,从官网下载
dubbo-demo结构
- dubbo-demo-api
- I:DemoService
- dubbo-demo-consumer
- Consumer
- dubbo-demo-consumer.xml
- dubbo.properties
- log4j.properties
- dubbo-demo-provider
- DemoServiceImpl
- Provider
- dubbo-demo-provider.xml
- dubbo.properties
- log4j.properties
Provider
注册/注销服务时序图
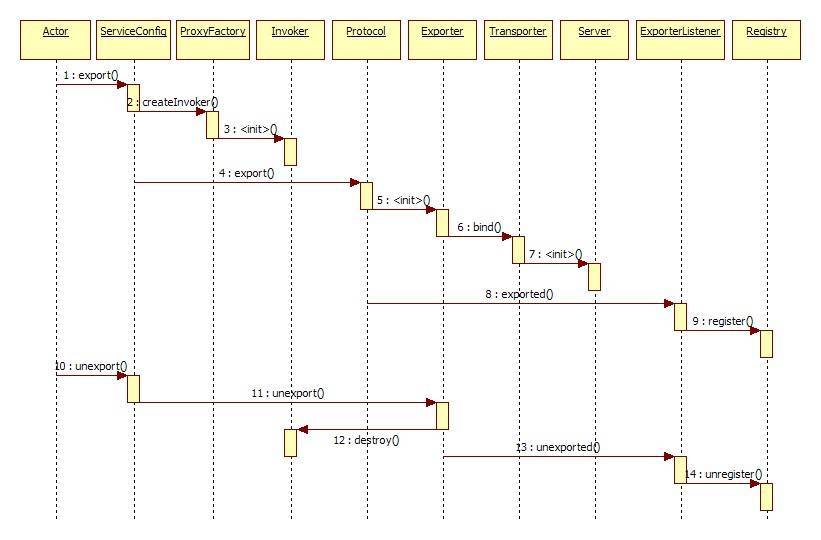
ServiceConfig -> ProxyFactory(JavassistProxyFactory/JdkProxyFactory) -> Invoker(AbstractProxyInvoker的实例) -> filter(exception,monitor等) -> RegistryProtocol(Dubbo,Hessian,Injvm,Rmi,WebService等) -> Exporter -> Transporter -> Server
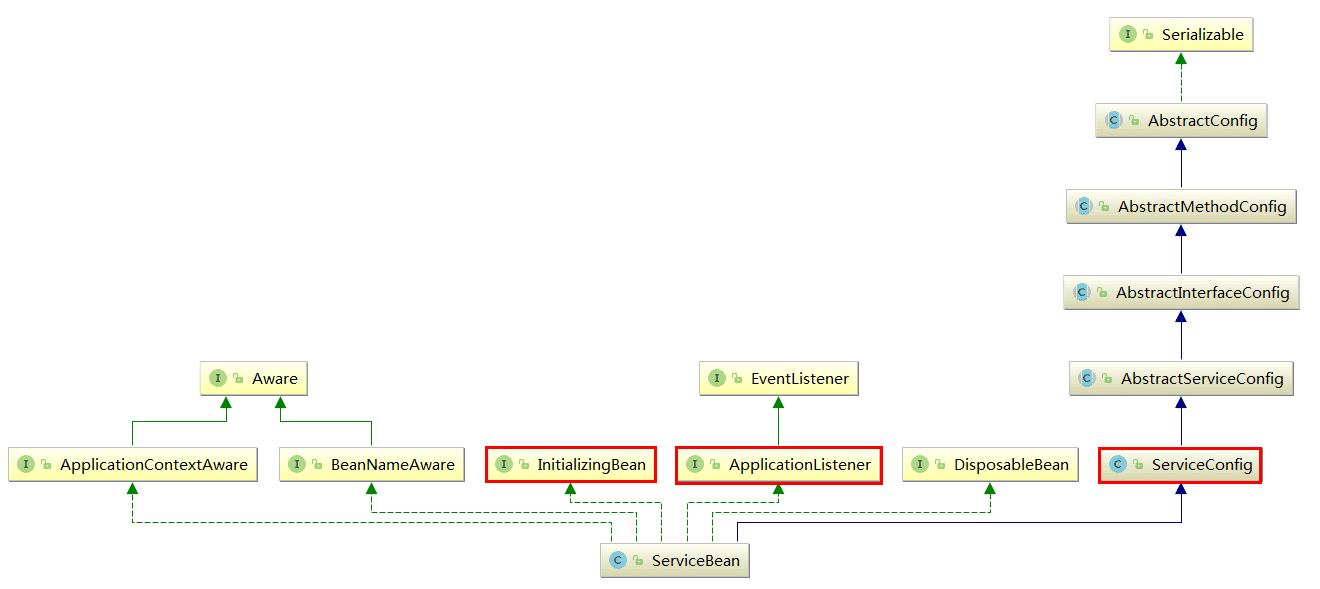
ServiceBean
URL
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL: 所有扩展点参数都包含URL参数,URL作为上下文信息贯穿整个扩展点设计体系。
属性有protocol、host、port、path、parameters、string等。
Protocol
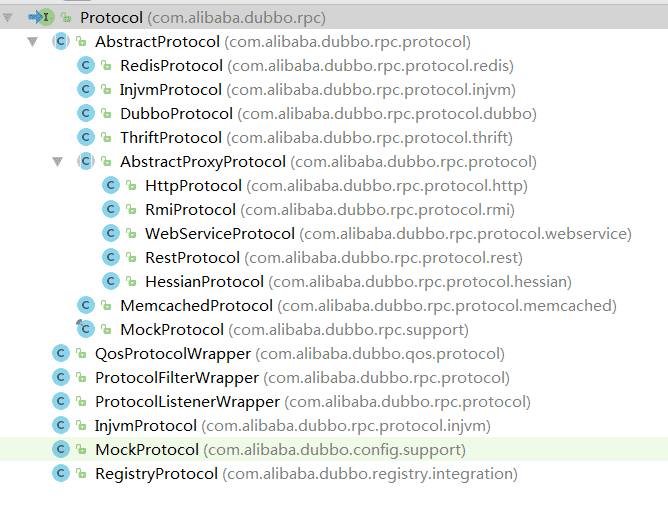
主要方法: Exporter
Invoker与Exporter
主要就是: 最外面用xxWrapper包xxExporter再包xxInvoker,Invoker最里面是个Wrapper(proxy:ref)
Invoker执行过程分成三种类型:
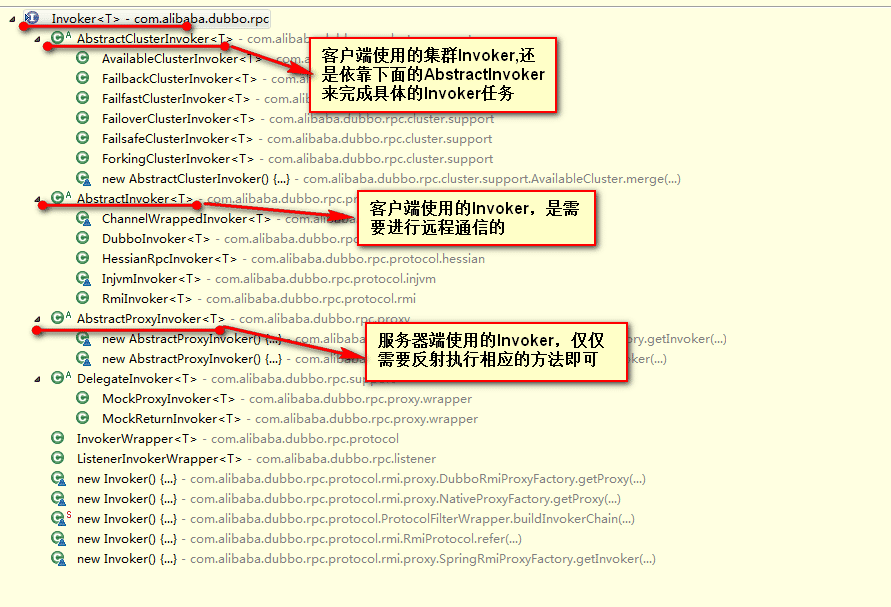
Exporter负责维护invoker的生命周期,只有Invoker<T> getInvoker()方法与void unexport()方法。
DEBUG
首先修改dubbo-demo-provider.xml配置文件,将dubbo:registry设置为zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
启动Provider的main方法。
(部分相关代码在步骤下贴出)
1 . ClassPathXmlApplicationContext设置xml地址。调用AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法。
2 . obtainFreshBeanFactory() -> refreshBeanFactory() -> loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory) ..-> registerBeanDefinitions(Document, Resource) -> parseBeanDefinitions(Element, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate)时判断ele不是DefaultNamespace,<dubbo:>下执行parseCustomElement(Element),获取dubbo的namespaceUrl,取到DubboNamespaceHandler执行DubboBeanDefinitionParser.parse方法生成BeanDefinition。分别有(ApplicationConfig,RegistryConfig, ProtocolConfig, ServiceBean)。
3 . refresh的finishBeanFactoryInitialization()方法进入,会预先初始化单例的bean,ServiceBean初始化过程会设置beanName,设置容器applicationContext,回调InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet。
4 . 在afterPropertiesSet方法里设置Provider、Application、Module、Registries、Monitor、Protocols、Path(beanName),再由isDelay判断是否立即export。
5 . refresh的finishRefresh()方法进入,publishEvent(..)当完成ApplicationContext初始化后,广播类ApplicationEventMulticaster广播ContextRefreshedEvent事件,以保证对应的监听器可以做进一步的逻辑处理,之前一步实例化的ServiceBean注册了这个事件,触发onApplicationEvent并调用export()暴露服务。
6 . 获取ProviderConfig的export属性,判断是否暴露,不暴露的话直接返回。获取ProviderConfig的delay属性,如果需要则delay几秒再调用doExport。否则立即调用doExport。如同spring命名风格,真正做事的是doxxx方法,所以进入doExport()。
protected synchronized void doExport() {
if (unexported) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already unexported!");
}
if (exported) {
return;
}
exported = true;
if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("<dubbo:service interface=\"\" /> interface not allow null!");
}
checkDefault();
if (provider != null) {
if (application == null) {
application = provider.getApplication();
}
if (module == null) {
module = provider.getModule();
}
if (registries == null) {
registries = provider.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = provider.getMonitor();
}
if (protocols == null) {
protocols = provider.getProtocols();
}
}
if (module != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = module.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = module.getMonitor();
}
}
if (application != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = application.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = application.getMonitor();
}
}
if (ref instanceof GenericService) {
interfaceClass = GenericService.class;
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(generic)) {
generic = Boolean.TRUE.toString();
}
} else {
try {
interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread()
.getContextClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods);
checkRef();
generic = Boolean.FALSE.toString();
}
if (local != null) {
if ("true".equals(local)) {
local = interfaceName + "Local";
}
Class<?> localClass;
try {
localClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(local);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(localClass)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The local implementation class " + localClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName);
}
}
if (stub != null) {
if ("true".equals(stub)) {
stub = interfaceName + "Stub";
}
Class<?> stubClass;
try {
stubClass = ClassHelper.forNameWithThreadContextClassLoader(stub);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (!interfaceClass.isAssignableFrom(stubClass)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The stub implementation class " + stubClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + interfaceName);
}
}
checkApplication();
checkRegistry();
checkProtocol();
appendProperties(this);
checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass);
if (path == null || path.length() == 0) {
path = interfaceName;
}
doExportUrls();
ProviderModel providerModel = new ProviderModel(getUniqueServiceName(), this, ref);
ApplicationModel.initProviderModel(getUniqueServiceName(), providerModel);
}
7 . 将exported设为true,防止重复导出这个服务。判断interfaceName为空则抛出异常。
8 . checkDefault()方法,appendProperties(provider)去读取xml配置(这里是dubbo.properties)设置到provider(ProviderConfig)属性中去。
9 . 判断接口的实现类ref是否是GenericService类型,代表泛化调用,设置interfaceClass为GenericService类型。否则,通过反射设置interfaceClass为调用dubbo的interface接口类型,然后checkInterfaceAndMethods检查配置的MethodConfig中的方法是否都在该interface中存在,checkRef检查ref对象是否实现了interface接口。
10 . local = interfaceName + “Local” 与 stub = interfaceName + “Stub”,反射判断是否实现interfaceClass接口(没进入)
11 . 向后兼容(for backward compatibility)ApplicationConfig、RegistryConfig、ProtocolConfig。appendProperties再设置属性到ServiceConfig,checkStubAndMock按字面意思,检查local,stub和mock。
12 . 调用doExportUrls()导出URL,进入方法。
13 . loadRegistries遍历所有的RegistryConfig,这里只配了zookeeper。遍历registries时,获取注册中心的ip地址列表,将path、protocol、dubbo版本、时间戳等放到map中。parseURLs根据ip和map转成对应个数的URL字串的列表。将URL协议头从zookeeper://设为registry://。返回registryURLsregistry://127.0.0.1:2181/com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=demo-provider&dubbo=2.0.0&pid=4612&qos.port=22222®istry=zookeeper×tamp=1532191131293。
private void doExportUrls() {
List<URL> registryURLs = loadRegistries(true);
for (ProtocolConfig protocolConfig : protocols) {
doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(protocolConfig, registryURLs);
}
}
14 . 遍历不同的ProtocolConfig(dubbo,rmi,http,hessian,injvm等),现在只配置了dubbo,执行doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(ProtocolConfig, List<URL>)方法。
15 . 建立map,放入各种参数(side, bind.ip, application, methods, qos.port, dubbo, interface, bind.port, anyhost等)。
16 . 获取host,findConfigedHosts(ProtocolConfig, List<URL>, Map<String, String>)会从registryURLs地址列表遍历,将可以socket成功连接的注册url设置为hostToBind,然后先从protocolConfig取默认ip,没有则返回hostToBind为host。获取port,从dubbo:protocol配置中获取。最后创建URL对象dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-provider&bind.ip=<registry-host>&bind.port=20880&dubbo=2.0.0&generic=false&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&
methods=sayHello&pid=8020&qos.port=22222&side=provider×tamp=1532191131293,从URL获取scope(null),如果scope是none则不导出。
String host = this.findConfigedHosts(protocolConfig, registryURLs, map);
Integer port = this.findConfigedPorts(protocolConfig, name, map);
URL url = new URL(name, host, port, (contextPath == null || contextPath.length() == 0 ? "" : contextPath + "/") + path, map);
if (ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ConfiguratorFactory.class)
.hasExtension(url.getProtocol())) {
url = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ConfiguratorFactory.class)
.getExtension(url.getProtocol()).getConfigurator(url).configure(url);
}
String scope = url.getParameter(Constants.SCOPE_KEY);
// don't export when none is configured
if (!Constants.SCOPE_NONE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
// export to local if the config is not remote (export to remote only when config is remote)
if (!Constants.SCOPE_REMOTE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
exportLocal(url);
}
// export to remote if the config is not local (export to local only when config is local)
if (!Constants.SCOPE_LOCAL.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Export dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " to url " + url);
}
if (registryURLs != null && registryURLs.size() > 0) {
for (URL registryURL : registryURLs) {
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent("dynamic", registryURL.getParameter("dynamic"));
URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(registryURL);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
url = url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, monitorUrl.toFullString());
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Register dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " url " + url + " to registry " + registryURL);
}
Invoker<?> invoker = proxyFactory.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, registryURL.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.EXPORT_KEY, url.toFullString()));
DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker wrapperInvoker = new DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker(invoker, this);
Exporter<?> exporter = protocol.export(wrapperInvoker);
exporters.add(exporter);
}
} else {
Invoker<?> invoker = proxyFactory.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, url);
DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker wrapperInvoker = new DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker(invoker, this);
Exporter<?> exporter = protocol.export(wrapperInvoker);
exporters.add(exporter);
}
}
}
this.urls.add(url);
17 . 判断scope不是remote,执行exportLocal(URL)本地暴露。首先根据dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数生成本地URLinjvm://127.0.0.1/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数。
if (!Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL.equalsIgnoreCase(url.getProtocol())) {
URL local = URL.valueOf(url.toFullString())
.setProtocol(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL)
.setHost(LOCALHOST)
.setPort(0);
ServiceClassHolder.getInstance().pushServiceClass(getServiceClass(ref));
Exporter<?> exporter = protocol.export(
proxyFactory.getInvoker(ref, (Class) interfaceClass, local));
exporters.add(exporter);
logger.info("Export dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " to local registry");
}
18 . 然后在ServiceClassHolder的ThreadLocal中放入ref引用的class(DemoServiceImpl)。
19 . 接着先从ProxyFactory(@SPI(“javassist”))(StubProxyFactoryWrapper)获取Invoker,内部调用JavassistProxyFactory.getInvoker,生成Wrapper包装proxy,返回AbstractProxyInvoker。然后通过Protocol(@SPI(“dubbo”))(ProtocolListenerWrapper去export,这里判断protocol(injvm)是否是registry,现在不是则返回ListenerExporterWrapper,里面通过ProtocolFilterWrapper同样判断protocol,不是则buildInvokerChain建立Filter链,最终通过调用InjvmProtocol去创建InjvmExporter返回。完成导出的Exporter放入exporters列表中。
// JavassistProxyFactory
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// TODO Wrapper cannot handle this scenario correctly: the classname contains '$'
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
// ProtocolListenerWrapper 返回ListenerExporterWrapper(Exporter<T>, List<ExporterListener>)
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(invoker.getUrl().getProtocol())) {
return protocol.export(invoker);
}
return new ListenerExporterWrapper<T>(protocol.export(invoker),
Collections.unmodifiableList(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExporterListener.class)
.getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), Constants.EXPORTER_LISTENER_KEY)));
}
// ProtocolFilterWrappe
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(invoker.getUrl().getProtocol())) {
return protocol.export(invoker);
}
return protocol.export(buildInvokerChain(invoker, Constants.SERVICE_FILTER_KEY, Constants.PROVIDER));
}
// InjvmProtocol 返回InjvmExporter(Invoker<T>, String, Map<String, Exporter<?>>)
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
return new InjvmExporter<T>(invoker, invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey(), exporterMap);
}
包装成:
ListenerExportWrapper( InjvmExporter( AbstractProxyInvoker( ... ), key, exporterMap[key, Invoker] ), List<ExporterListener )
AbstractProxyInvoker内部有: proxy:DemoServiceImpl, type:interfaceClass, url: injvm://127.0.0.1/..., wrapper等。
且为InvokerChain链,拥有next的Invoker引用,内部为filter实现调用。
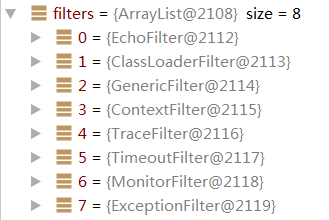 20 . export to remote if the config is not local,由于scope为null,所以继续。
20 . export to remote if the config is not local,由于scope为null,所以继续。
21 . 遍历registryURLs所有地址列表,加载monitor,设置参数导出MonitorURL,如果有Monitor则给注册url设置monitor参数。
22 . 根据服务具体实现ref、实现接口interfaceClass、regitryUrl从代理工厂ProxyFactory(@SPI(“javassist”))(StubProxyFactoryWrapper)获取代理Invoker,依旧默认使用javassist库做反射(URL.getParameter:defaultValue),通过JavassistProxyFactory.getInvoker()获取Invoker。
23 . 包装成DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker(Invoker<T>, ServiceConfig)。执行protocol.export(Invoker<T>),依旧通过ProtocolListenerWrapper去export,这次判断protocol是registry,通过ProtocolFilterWrapper判断后进入RegistryProtocol.export(final Invoker<T>)。
包装成: originInvoker
DelegoteProviderMetaDataInvoker( AbstractProxyInvoker( ..., registry://127.0.0.1:2181/.. ), serviceConfig:this )
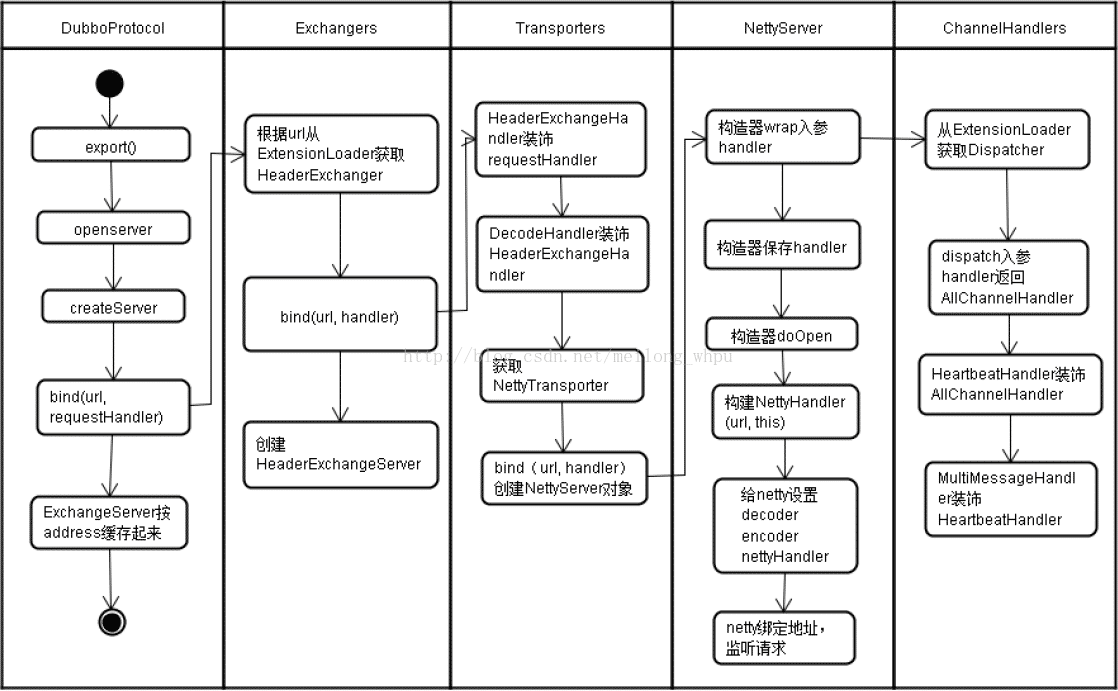
24 . 先导出invoker暴露服务,先按key(dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数)从本地map缓存中取,没有则生成Invoker,使用protocol.export导出,然后放入map中。这里使用DubboProtocol,先根据invoker的url生成cacheKey(com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService:20880),再根据invoker、cacheKey、exporterMap创建一个DubboExporter按key放入exporterMap中,从URL中判断是否是代理支持的事件和是否是回调服务。这里都不是。然后调用openServer(URL)方法根据Url创建一个Server放入serverMap,key为(<registry-host>:20880)。createServer,默认使用netty,dubbo协议。启动Server。最后optimizeSerialization给url加上参数。
包装成:
ExporterChangeableWrapper( ListenerExporterWrapper( DubboExporter( InvokerDelegete( originInvoker, url ), key, exporterMap[key, invoker] ), List<ExporterListener> ) )
InvokerDelegete内url: dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/...,originInvoker为前面包装后的Invoker。且为InvokerChain链,拥有next的Invoker引用,内部为filter实现调用。
// DubboProtocol
createServer(URL url) ->
server = Exchangers.bind(url, requestHandler)
// Exchangers
return getExchanger(url).bind(url, handler);
// HeaderExchanger
return new HeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))));
// startHeatbeatTimer()
// Transporters
// 有Grizzly、Mina、Netty4、Netty(走了这个)
return getTransporter().bind(url, handler);
// NettyTransporter
return new NettyServer(url, listener);
// 创建server监听,NettyHandler处理Channel的连接/关闭,读/写事件
NettyServer.doOpen()
// pipeline.addLast("handler", nettyHandler)
这里传给netty的listener是DubboProtocol内部定义的一个ExchangeHandler
里面的reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message)方法为主要执行方法。接收事件后会到这个方法内执行,或者调用父类super.received(channel, message)。
所以当netty接受到请求时,会先
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv)获取,方法里生成serviceKey,从exporterMap里获取exporter,再返回exporter.getInvoker()
最后执行invoker.invoke(Invocation),一路跟上去,包括一个invokerchain的filter处理链,
最后就是执行JavassistProxyFactory里生成的AbstractProxyInvoker的doInvoke方法。
内部执行wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments)反射执行,proxy为DemoServiceImpl。
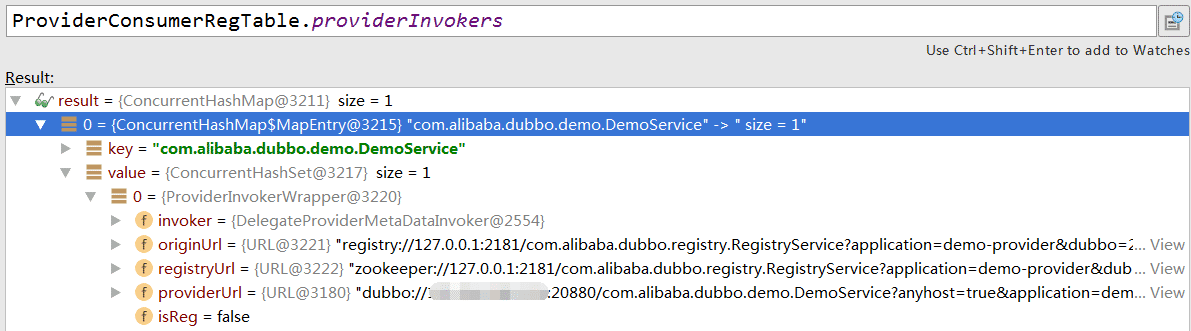
 25 . 回到RegistryProtocol,再注册provider,从originInvoker获取registryUrl(
25 . 回到RegistryProtocol,再注册provider,从originInvoker获取registryUrl(zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?参数),Registry(ZookeeperRegistry)与registedProviderUrl(dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数),放入ProviderConsumerRegTable的本地providerInvokers(ConcurrentHashMap)中,判断是否延迟暴露,非延迟则registry.register(registedProviderUrl)完成注册(ZookeeperRegistry.doRegister(url),通过zkClient创建URL对应节点)[^1](消费者在消费服务时会根据消费的接口名找到对应的zookeeper节点目录,对目录进行监听,接收推送),将ProviderConsumerRegTable中取出ProviderWrapper设置reg为true。
// RegistryProtocol
public <T> Exporter<T> export(final Invoker<T> originInvoker) throws RpcException {
//export invoker
final ExporterChangeableWrapper<T> exporter = doLocalExport(originInvoker);
URL registryUrl = getRegistryUrl(originInvoker);
//registry provider
final Registry registry = getRegistry(originInvoker);
final URL registedProviderUrl = getRegistedProviderUrl(originInvoker);
//to judge to delay publish whether or not
boolean register = registedProviderUrl.getParameter("register", true);
ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerProvider(originInvoker, registryUrl, registedProviderUrl);
if (register) {
register(registryUrl, registedProviderUrl);
ProviderConsumerRegTable.getProviderWrapper(originInvoker).setReg(true);
}
// Subscribe the override data
// FIXME When the provider subscribes, it will affect the scene : a certain JVM exposes the service and call the same service. Because the subscribed is cached key with the name of the service, it causes the subscription information to cover.
// 当提供者订阅时,它将影响场景:某个JVM公开服务并调用相同的服务。因为订阅是用服务的名称缓存的,所以它会导致订阅信息被覆盖。
final URL overrideSubscribeUrl = getSubscribedOverrideUrl(registedProviderUrl);
final OverrideListener overrideSubscribeListener = new OverrideListener(overrideSubscribeUrl, originInvoker);
overrideListeners.put(overrideSubscribeUrl, overrideSubscribeListener);
registry.subscribe(overrideSubscribeUrl, overrideSubscribeListener);
//Ensure that a new exporter instance is returned every time export
return new DestroyableExporter<T>(exporter, originInvoker, overrideSubscribeUrl, registedProviderUrl);
}
26 .
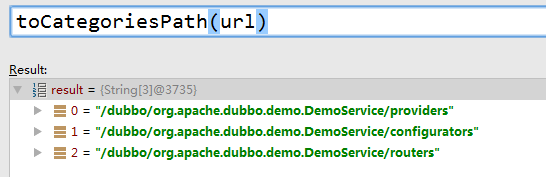
去发布订阅时覆盖数据,按registedProviderUrl创建overrideSubscribeUrl(provider://<registry-host>:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数)和OverrideListener,执行registry.subscribe(URL, NotifyListener),通过FailbackRegistry去执行ZookeeperRegistry.doSubscribe发送一个订阅请求,在zk上创建/dubbo/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService/configurators节点[^2],添加子节点Listener,如果节点下有修改触发notify。
List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>();
for (String path : toCategoriesPath(url)) {
ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
if (listeners == null) {
zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener>());
listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
}
ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
if (zkListener == null) {
listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, new ChildListener() {
public void childChanged(String parentPath, List<String> currentChilds) {
ZookeeperRegistry.this.notify(url, listener, toUrlsWithEmpty(url, parentPath, currentChilds));
}
});
zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
}
zkClient.create(path, false);
List<String> children = zkClient.addChildListener(path, zkListener);
if (children != null) {
urls.addAll(toUrlsWithEmpty(url, path, children));
}
}
notify(url, listener, urls);
27 . 然后notify(URL, NotifyListener, List<URL>),调用AbstractRegistry.notify,获取URL的category作为key,将urls放入map的value中。遍历map结果,本地的file文件保存version等属性(同步/异步线程池保存)。调用OverrideListener.notify(List<URL>),获取当前currentUrl(可能已被多次覆盖)与newUrl(此次配置),如果不一致,doChangeLocalExport(originInvoker, newUrl),重新导出invoker。
28 . 回到RegistryProtocol,组装成DestroyableExporter(Exporter<T> exporter, Invoker<T> originInvoker, URL subscribeUrl, URL registerUrl)返回,类实现了unexport方法。返回Exporter。
29 . 回到ServiceConfig,向exporters中加入导出完成的Exporter,此时就有2个了,一个是本地ListenerExportWrapper,一个是注册到远程ZK的Registryprotocol$ExporterChangeableWrapper,最后在ServiceConfig的urls加入 dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数。
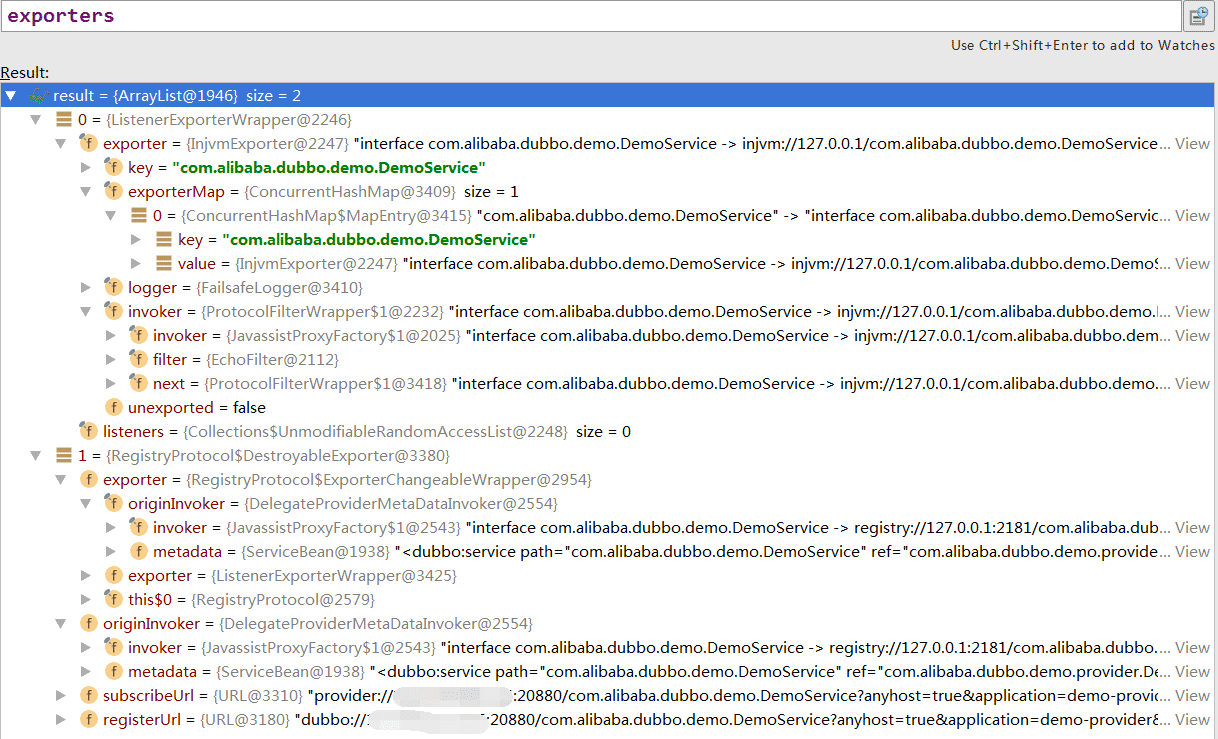 30 . 创建ProviderModel(String serviceName, ServiceConfig metadata, Object serviceInstance),初始化initProviderModel,放入ApplicationModel的providedServices(ConcurrentMap)中,key为com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService,value为ProviderModel。
30 . 创建ProviderModel(String serviceName, ServiceConfig metadata, Object serviceInstance),初始化initProviderModel,放入ApplicationModel的providedServices(ConcurrentMap)中,key为com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService,value为ProviderModel。
zookeeper下node结构
^1:
/dubbo
/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService
/providers[dubbo://xxx.xxx.xxx.xx:20880/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-provider&dubbo=2.0.0&generic=false&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=8376&side=provider×tamp=1532179751055]
^2:
/dubbo
/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService
/providers
/configurators[]
Consumer
服务订阅/取消时序图
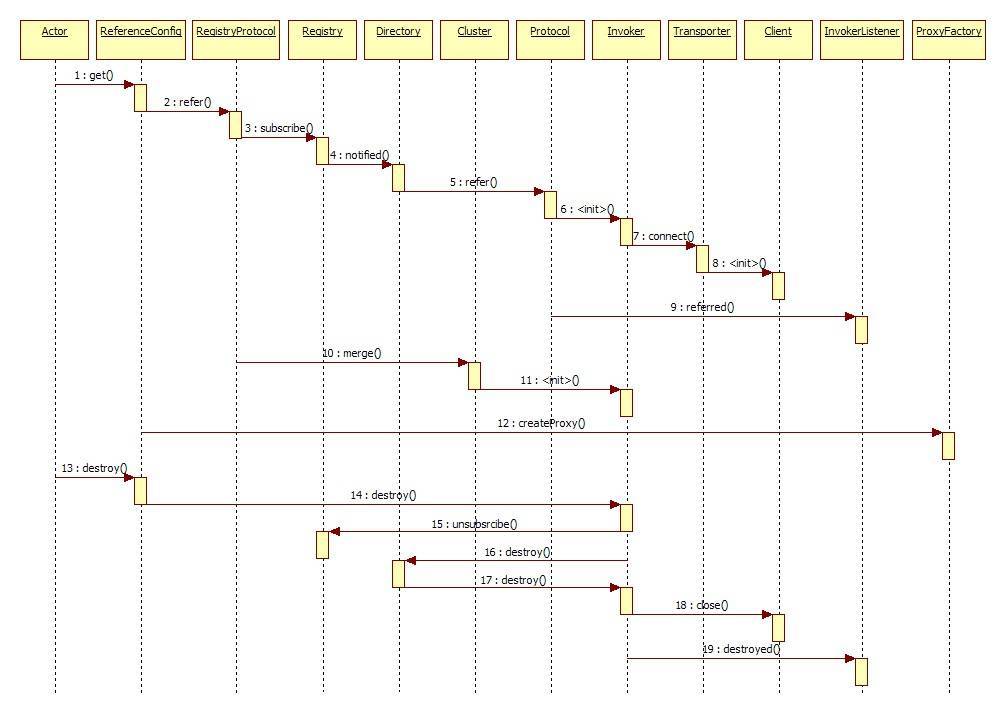
jdk dynamic proxy -> cluster -> directory -> registry -> router -> loadbalance -> filter(monitor等) -> invoker -> client -> transporter -> codec
DEBUG
首先修改dubbo-demo-consumer.xml配置文件,将dubbo:registry设置为zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
启动Consumer的main方法。
使用IDEA时,DEBUG代码,在ReferenceConfig的init方法里initialized莫名会为true,导致本来为只初始化一次的方法被直接跳出了,在ReferenceConfig的构造方法里打断点,发现那时候的initialized已经为true了,后台日志在AbstractConfig.toString会报一个InvocationTargetException,非常不解。于是网上查了下,刚好有位老兄遇到了这个问题。知道了问题,所以只要去Settings - Build,Execution,Deployment - Debugger - Data Views - Java去把enable tostring() object view关掉就行了。
(部分相关代码在步骤下贴出)
1 . 同Provider一样,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext初始化,生成BeanDefinition,消费端按配置生成ApplicationConfig、RegistryConfig、ReferenceBean。然后创建单例Bean。
2 . ReferenceBean实现了InitializingBean,初始化ReferenceBean时调用afterPropertiesSet方法,设置Consumer、Application、Module、Registries、Monitor。如果配置了init=”true”,直接调用getObject()来触发init方法。
3 . 调用context.start(),通过委托给LifecycleProcessor来start(默认在finishRefresh委托执行onRefresh,最后都会执行startBeans方法)。触发ContextStartedEvent,实现ApplicationListener
4 . context.getBean(“demoService”)获取实现service,在AbstractBeanFactory.getObjectForBeanInstance时会判断是否实现FactoryBean接口,由于ReferenceBean实现了FactoryBean,调用其getObject()的返回结果作为实例。
5 . 在关闭idea的enable tostring后debug,这边就不会进坑了。走进ReferenceConfig的init方法。
6 . 设置各种参数,与serviceBean开始的差不多,读取XML配置设置到ReferenceConfig的属性中,判断是否是Generic并设置interfaceClass,获取resolveFile,设置application、module、registries、monitor。兼容之前版本Application。设置map,放入application、register.ip、interface、methods等参数。将attributes存入systemContext。
7 . 执行createProxy(Map<String, String>)创建代理对象。
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
URL tmpUrl = new URL("temp", "localhost", 0, map);
final boolean isJvmRefer;
if (isInjvm() == null) {
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // if a url is specified, don't do local reference
isJvmRefer = false;
} else if (InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl)) {
// by default, reference local service if there is
isJvmRefer = true;
} else {
isJvmRefer = false;
}
} else {
isJvmRefer = isInjvm().booleanValue();
}
if (isJvmRefer) {
URL url = new URL(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // user specified URL, could be peer-to-peer address, or register center's address.
String[] us = Constants.SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url);
if (us != null && us.length > 0) {
for (String u : us) {
URL url = URL.valueOf(u);
if (url.getPath() == null || url.getPath().length() == 0) {
url = url.setPath(interfaceName);
}
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
} else {
urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map));
}
}
}
} else { // assemble URL from register center's configuration
List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false);
if (us != null && !us.isEmpty()) {
for (URL u : us) {
URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
map.put(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString()));
}
urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
}
}
if (urls.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config.");
}
}
if (urls.size() == 1) {
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else {
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
for (URL url : urls) {
invokers.add(refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url));
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; // use last registry url
}
}
if (registryURL != null) { // registry url is available
// use AvailableCluster only when register's cluster is available
URL u = registryURL.addParameter(Constants.CLUSTER_KEY, AvailableCluster.NAME);
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));
} else { // not a registry url
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers));
}
}
}
Boolean c = check;
if (c == null && consumer != null) {
c = consumer.isCheck();
}
if (c == null) {
c = true; // default true
}
if (c && !invoker.isAvailable()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to check the status of the service " + interfaceName + ". No provider available for the service " + (group == null ? "" : group + "/") + interfaceName + (version == null ? "" : ":" + version) + " from the url " + invoker.getUrl() + " to the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refer dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from url " + invoker.getUrl());
}
// create service proxy
return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
}
8 . 按map生成一个URL,判断是否调用本地JVM引用对象。如果是的话就生成本地injvm的URL,protocol.refer生成invoker。这里没有配置是false,所以走另一个分支。
10 . 如果url不为null,就说明是我们指定的地址,可以是点对点的地址,也可以是注册中心的地址,放入urls。由于没有指定,所以去注册中心(ZK)获取地址。
11 . 调用loadRegistries,根据xml中配置的生成注册中心URL放入registryList并返回。在外面将返回列表遍历,放入map作为参数生成URL(registry://127.0.0.1:2181/..RegistryService?参数),放入urls。
12 . 判断urls的size,如果大于1条,说明有多个注册中心,每个都执行protocol.refer放入列表,查看是否是registry协议,使用最后一个作为registryUrl。如果存在注册地址registryURL,给URL加入参数。最后都调用Cluster.join(Directory
13 . 因为urls的size为1,所以直接调用refer方法。与export一样,先从ProtocolFilterWrapper判断protocol是否是registry,然后在ProtocolListenerWrapper中判断protocol是否是registry,最后进入RegistryProtocol的refer方法。
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
url = url.setProtocol(url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REGISTRY)).removeParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY);
Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url);
if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) {
return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url);
}
// group="a,b" or group="*"
Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(Constants.REFER_KEY));
String group = qs.get(Constants.GROUP_KEY);
if (group != null && group.length() > 0) {
if ((Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(group)).length > 1
|| "*".equals(group)) {
return doRefer(getMergeableCluster(), registry, type, url);
}
}
return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url);
}
14 . 生成URL(zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=demo-consumer&dubbo=2.0.2&pid=4644&qos.port=33333&refer=application=demo-consumer&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=4644&qos.port=33333®ister.ip=<registry-host>&side=consumer×tamp=1532489198935×tamp=1532500701557),按照URL创建Registry,AbstractRegistryFactory.getRegistry去调用ZookeeperRegistryFactory.createRegistry(URL)创建一个ZookeeperRegistry。
// super(url) -> FailbackRegistry
doRegister(url);
// -> ZookeeperRegistry
zkClient.create(toUrlPath(url), url.getParameter(Constants.DYNAMIC_KEY, true));
// ZookeeperRegistry构造方法
super(url);
if (url.isAnyHost()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("registry address == null");
}
String group = url.getParameter(Constants.GROUP_KEY, DEFAULT_ROOT);
if (!group.startsWith(Constants.PATH_SEPARATOR)) {
group = Constants.PATH_SEPARATOR + group;
}
this.root = group;
// 创建连接
zkClient = zookeeperTransporter.connect(url);
// 添加监听器,状态改变时恢复register与subscribe
zkClient.addStateListener(new StateListener() {
@Override
public void stateChanged(int state) {
if (state == RECONNECTED) {
try {
recover();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
});
15 . 如果获取的interfaceClass是RegistryService,则直接proxyFactory.getInvoker(T proxy, Class
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
// all attributes of REFER_KEY
Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getUrl().getParameters());
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(Constants.CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters);
if (!Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())
&& url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
registry.register(subscribeUrl.addParameters(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.CONSUMERS_CATEGORY,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)));
}
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY,
Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory);
ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory);
return invoker;
}
16 . 按class与url(zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/..RegistryService?参数)创建RegistryDirectory,生成subscribeUrl(consumer://<registry-host>/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?application=demo-consumer&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=7420&qos.port=33333&side=consumer×tamp=1532503429357)。
17 . 执行registry.register将subscribeUrl注册到zk。与provider执行的一样,调用FailbackRegistry再调用ZookeeperRegistry.doRegister(URL),把消费者注册到注册中心。URL放在zk的dubbo/…/consumers内。
18 . 调用directory.subscribe订阅地址(consumer://<registry-host>/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数),调用到RegistryDirectory,传入url与自己作为listener去调用FailbackRegistry的subscribe方法。最后调用ZookeeperRegistry的doSubscribe方法。
19 . 与provider执行的一样,这里创建zk节点,并添加监听器监听注册中心的节点变化。由于参数category=providers,configurators,routers,所以会创建3个zk节点。
消费端本地会缓存远程服务提供者(每个提供者对应一个Invoker对象)、注册中心配置、路由配置信息。监听注册中心路径是/dubbo/interfaceClass/providers和/dubbo/{interfaceClass}/configurators,/dubbo/${interfaceClass}/routers的节点,当提供者、配置、路由信息发生变化之后注册中心会通知消费者刷新本地缓存。Dubbo框架通过在消费端缓存提供者的信息消除对注册中心的强依赖,即使注册中心挂了服务依然可用。
20 . 与provider执行的一样,调用notify(url, listener, urls),通过FailbackRegistry调用AbstractRegistry的notify方法。将3个category与URL作为K,V放入map中,遍历map,写入文件且加锁保证只有一个线程执行,调用listener.notify执行RegistryDirectory.notify(List
21 . 进入RegistryDirectory.notify方法,创建invokerUrls(dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=6636&side=provider×tamp=1532569637175)。根据category为configurators或routers处理configurators或routers。重写overrideDirectoryUrl(zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?anyhost=true&application=demo-consumer&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=2120&qos.port=33333®ister.ip=<registry-host>&remote.timestamp=1532569637175&side=consumer×tamp=1532569691571)。执行refreshInvoker(List
22 . 当category为providers时,invokerUrls不为空,继续执行不跳出。执行toInvokers方法,将invokerURL转化为Invoker map。规则如下:
- 如果URL已转换为invoker,则不再从缓存中直接引用和获取,并注意URL中的任何参数更改将被重新引用。
- 如果传入的invoker列表不是空的,则意味着它是最新的调用列表。
- 如果传入的invokerURL列表为空,则意味着该规则仅是重写规则或路由规则,需要重新对比以决定是否重新引用。
23 . 因为第一次调用,肯定不在缓存内,因此创建一个InvokerDelegate(Invoker<T> invoker, URL url, URL providerUrl),其中url(dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-consumer&check=false&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=5092&qos.port=33333®ister.ip=<registry-host>&remote.timestamp=1532569637175&side=consumer×tamp=1532573298293),providerUrl(dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=demo-provider&dubbo=2.0.2&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService&methods=sayHello&pid=6636&side=provider×tamp=1532569637175),invoker调用protocol.refer去生成。
24 . 依旧通过ProtocolFilterWrapper(buildInvokerChain),ProtocolListenerWrapper(ListenerInvokerWrapper)调用到DubboProtocol的refer方法。创建了一个DubboInvoker(Class
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
optimizeSerialization(url);
// create rpc invoker.
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
25 . 获取参数ExchangeClient,执行getClients(url)。通过URL中connections参数确定创建多少连接。创建ExchangeClient,调用getSharedClient,里面调用initClient -> Exchangers.connect -> HeaderExchanger.connect创建一个HeaderExchangeClient(Client client, boolean needHeartbeat)。调用Transporters.connect,最后调用NettyTransporter.connect(URL url, ChannelHandler listener)创建一个NettyClient。doOpen()启动,connect()连接。返回的client包装成ReferenceCountExchangeClient,放入map,key为Address(
26 . 在RegistryDirectory中将返回的invoker按key(dubbo://<registry-host>:20880/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService?参数)放入newUrlInvokerMap。
26 . 回到RegistryDirectory继续执行toMethodInvokers,将invokers转换为与method关联的map。调用destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap, newUrlInvokerMap)方法。检查缓存中的invoker是否需要销毁。如果url参数autodestroy=false则invokers只会增加,可能会refer泄露。
27 . 回到RegistryProtocol,RegistryProtocol.doRefer方法后面调用cluster.join(directory)。MockClusterWrapper.join -> FailoverCluster.join创建FailoverClusterInvoker(Directory
28 . 最后调用ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory),在ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer里加入key(org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService),v(Set
29 . 一路返回invoker回到ReferenceConfig的createProxy方法最后,调用proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker)生成代理类,依旧是StubProxyFactoryWrapper.getProxy方法进入,调用AbstractProxyFactory.getProxy,还是使用Javassist库,调用JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy(Invoker
30 . 在ReferenceConfig的init方法最后,创建ConsumerModel(String serviceName,ReferenceConfig metadata, Object proxyObject, Method[] methods)对象,并初始化放到consumedServices(ConcurrentMap)中。
方法调用
Counsumer端请求
dubbo 2.7.0版本 用的netty4.NettyClient
1 . Consumer中执行方法demoService.sayHello(“world”)进行方法调用。由于是动态代理类,所以执行InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke方法。
2 . 如果是toString、hashCode、equals方法,直接调用MockClusterInvoker对应方法。判断类有没实现@AsyncFor或方法名以Async结尾或返回CompletableFuture类型。不是则创建一个RpcInvocation。执行invoker.invoke。调用到MockClusterInvoker.invoke(Invocation)方法。
3 . 获取url的mock参数,如果是force则direct mock执行doMockInvoke,其他如果是fail-mock则调用invoker.invoke,失败了也执行doMockInvoke,默认为false是no mock。这里应该是为了用于服务降级,对应dubbo monitor中的动态配置。
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
String value = directory.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (value.length() == 0 || value.equalsIgnoreCase("false")) {
//no mock
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} else if (value.startsWith("force")) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.info("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl());
}
//force:direct mock
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
} else {
//fail-mock
try {
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
} else {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl(), e);
}
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e);
}
}
}
return result;
}
4 . 所以这里走默认执行AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke,先调用checkInvokers()检查对应的invokers是否为空,为空则抛出没有provider的异常日志,然后获取LoadBalance。默认是random,调用ExtensionLoader.getExtension -> createExtension从EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz)里获取RandomLoadBalance。
5 . 执行FailoverClusterInvoker的doInvoke方法。
cluster主要将directory中的多个invoker封装成一个,区分不同的失败重试策略。常用的cluster集群容错架构:
- FailoverCluster: 默认cluster。失败自动切换,当出现失败,重试其它服务器,默认重试3次
- FailfastCluster: 快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错,用于非幂等性操作,比如网络情况不好,写操作)
- Failsafe: 失败安全,报异常时直接忽略,用于写入日志等
- Failback Cluster: 失败自动恢复
- Forking Cluster: 并行调用多个,一个成功就返回
- Broadcst Cluster: 广播调用,任何一个报错则报错,比如更新缓存等
5 . 获取失败次数,URL中retries配置,没有默认2+1次。
// retry loop.
RpcException le = null; // last exception.
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers.
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`.
//NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy.
if (i > 0) {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
copyinvokers = list(invocation);
// check again
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
}
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Although retry the method " + invocation.getMethodName()
+ " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress()
+ ", but there have been failed providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le);
}
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
6 . 第1次调用时,直接执行AbstractClusterInvoker.select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker
7 . 如果是第2+次调用,就要调用AbstractClusterInvoker.list(Invocation)方法(其实是FailoverClusterInvoker)。调用AbstractDirectory.list方法(其实是RegistryDirectory,Directory有两种,StaticDirectory用于多个注册中心; RegistryDirectory,代表一组可以用的invoker,有notify方法,用于注册中心的回调,修改methodInvokerMap来存储动态变化的多个invoker或者router路由的变化,回调在RegistryDirectory.notify()中执行),里面再调用RegistryDirectory.doList方法里通过methodInvokerMap(local reference)中找出所有的invoker,在AbstractDirectory.list中继续通过遍历localRouters(分为Script和Condition两种,Condition路由就是管理后台配置的路由规则,比如对于某个service,当消费端的ip满足什么条件调用满足对应条件的服务端.可以启用或者禁用某条路由规则),调用调用MockInvokersSelector.route -> MockInvokersSelector.getNormalInvokers找出可以执行的invoker。
8 . 返回多个符合条件的invoker。和第1次调用一样,进入select方法,内部会调用loadbalance.select执行负载均衡,从中挑选一个invoker返回,默认是进入RandomLoadBalance.doSelect()随机算法(负载均衡算法包括random(随机)、roundrobin(R-R循环)、leastactive(最不活跃)、consistenthash(一致性hash))。将返回的Invoker加入Invoker列表,在RpcContext的ThreadLocal
9 . 执行invoker.invoke(Invocation),InvokerWrapper持有ProtocolFilterWrapper链,保存的是持有DubboInvoker(dubbo协议)的InvokerDelegete对象,在Invoker-Filter链的头部。所以调用从InvokerWrapper.invoke -> ProtocolFilterWrapper的filter链中调用filter.invoke -> ConsumerContextFilter/FutureFilter/MonitorFilter -> AbstractInvoker.invoke -> DubboInvoker.doInvoke方法。
10 . 在DubboInvoker.doInvoke()中先获取当前调用的ExchangeClient,如果有多个Client,按顺序选一个。判断调用是不是异步的,异步回调的,单向的。获取超时时间,没有配置默认1000毫秒。
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version);
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
boolean isAsyncFuture = RpcUtils.isGeneratedFuture(inv) || RpcUtils.isFutureReturnType(inv);
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (isOneway) {
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return new RpcResult();
} else if (isAsync) {
ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout);
// For compatibility
FutureAdapter<Object> futureAdapter = new FutureAdapter<>(future);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(futureAdapter);
Result result;
if (isAsyncFuture) {
// register resultCallback, sometimes we need the asyn result being processed by the filter chain.
result = new AsyncRpcResult(futureAdapter, futureAdapter.getResultFuture(), false);
} else {
result = new SimpleAsyncRpcResult(futureAdapter, futureAdapter.getResultFuture(), false);
}
return result;
} else {
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get();
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
11 . 远程调用分三种类型:
- 单向调用: 无需获取调用结果,也无需等待接口返回结果(不单返回值,异常也是调用结果),调用后返回new RpcResult()
- 异步调用: 需要返回结果,不同步等待接口调用结束,给调用者返回一个Future,但不等待Future.get返回调用结果。根据isAsyncFuture分别创建AsyncRpcResult或SimpleAsyncRpcResult。
- 同步调用: 同步等待服务调用结束获取调用结果,给调用者返回一个Future并且Future.get等待结果,此时接口调用线程会挂起等待响应 执行currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get()得到服务端返回结果Result。
12 . ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request(Object request, int timeout) -> HeaderExchangeClient.request -> HeaderExchangeChannel.request方法,其中request参数是RpcInvocation对象,timeout接口超时时间。创建Request对象,将这些参数放入。创建DefaultFuture(Channel channel, Request request, int timeout)。调用channel.send(req)发送请求。channel为netty4.NettyClient。
13 . AbstractPeer.send -> AbstractClient.send(),getChannel()获取Channel(服务端打交道的NettyClient实例),调用channel.send -> netty4.NettyChannel.send,检查channel是否关闭,调用channel.writeAndFlush(message)发送。AbstractChannel.writeAndFlush -> DefaultChannelPipeline.writeAndFlush -> AbstractChannelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush,里面调用write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise)方法。调用AbstractChannelHandlerContext.WriteAndFlushTask.newInstance(next, m, promise)返回task,AbstractChannelHandlerContext调用safeExecute(EventExecutor executor, Runnable runnable, ChannelPromise promise, Object msg)方法。
14 . 回到DubboInvoker的doInvoke获取到ResponseFuture后调用get方法,到DefaultFuture的get方法。里面暂停在done.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)。
15 . FastThreadLocalRunnable.run -> NioEventLoop.run -> SingleThreadEventExecutor.runAllTasks -> AbstractEventExecutor.run执行task,AbstractChannelHandlerContext.write -> AbstractChannelHandlerContext.write、invokeWrite -> 调用到NettyClientHandler.write方法。再一直往上走到MessageToByteEncoder.write方法,调用this.encode(ctx, cast, buf)进行编码。调用NettyCodecAdapter.encode -> DubboCountCodec.encode -> ExchangeCodec.encode、encodeRequest进行dubbo协议的编码,通过ChannelBuffer生成ChannelBufferOutputStream,serialization.serialize(Hessian2Serialization)拿到ObjectOutput,然后执行DubboCodec.encodeRequestData封装数据部分,然后把封装好的ChannelBuffer写到链路发送到服务端。
// NettyCodecAdapter
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
org.apache.dubbo.remoting.buffer.ChannelBuffer buffer = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(out);
Channel ch = ctx.channel();
NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ch, url, handler);
try {
codec.encode(channel, buffer, msg);
} finally {
NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ch);
}
}
// ExchangeCodec
protected void encodeRequest(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Request req) throws IOException {
Serialization serialization = getSerialization(channel);
// header.
byte[] header = new byte[HEADER_LENGTH];
// set magic number.
Bytes.short2bytes(MAGIC, header);
// set request and serialization flag.
header[2] = (byte) (FLAG_REQUEST | serialization.getContentTypeId());
if (req.isTwoWay()) header[2] |= FLAG_TWOWAY;
if (req.isEvent()) header[2] |= FLAG_EVENT;
// set request id.
Bytes.long2bytes(req.getId(), header, 4);
// encode request data.
int savedWriteIndex = buffer.writerIndex();
buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH);
ChannelBufferOutputStream bos = new ChannelBufferOutputStream(buffer);
ObjectOutput out = serialization.serialize(channel.getUrl(), bos);
if (req.isEvent()) {
encodeEventData(channel, out, req.getData());
} else {
encodeRequestData(channel, out, req.getData(), req.getVersion());
}
out.flushBuffer();
if (out instanceof Cleanable) {
((Cleanable) out).cleanup();
}
bos.flush();
bos.close();
int len = bos.writtenBytes();
checkPayload(channel, len);
Bytes.int2bytes(len, header, 12);
// write
buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex);
buffer.writeBytes(header); // write header.
buffer.writerIndex(savedWriteIndex + HEADER_LENGTH + len);
}
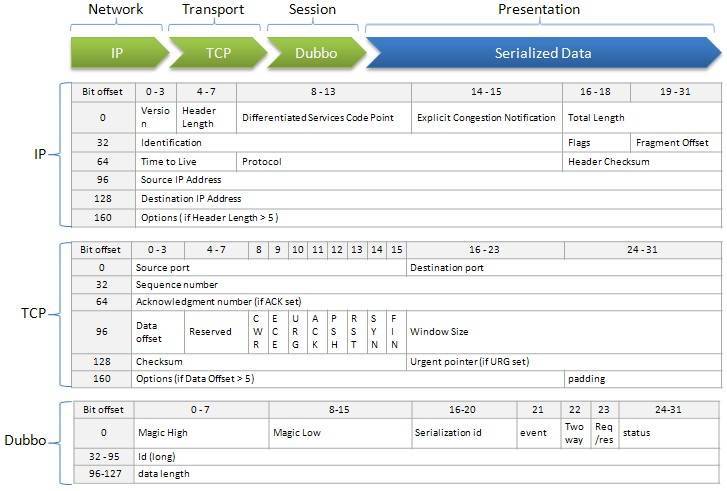
根据协议,消息中写入16个字节的消息头:
a、1-2字节,固定的魔数
b、第3个字节,第8位存储数据类型是请求数据还是响应数据,其它7位存储序列化类型,约定和服务端的序列化-反序列化协议
c、5-12个字节,请求id
d、13-16个字节,请求数据长度.框架中默认的序列化协议是hessian2。
消息体数据包含dubbo版本号、接口名称、接口版本、方法名称、参数类型列表、参数、附加信息,
把它们按顺序依次序列化,数据写入到类型为ChannelBuffer的buffer参数中
16 . 回到MessageToByteEncoder执行ctx.write(buf, promise)。回到NettyClientHandler执行handler.sent(channel, msg),一直调用到DefaultFuture.sent方法。
dubbo 2.6.0版本 用的netty.NettyClient
13 . AbstractPeer.send -> AbstractClient.send(),getChannel()获取Channel(服务端打交道的NettyClient实例),调用channel.send -> netty.NettyChannel.send,检查channel是否关闭,调用channel.write(message)发送。AbstractChannel.write -> Channels.write -> DefaultChannelPipeline.sendDownstream -> SimpleChannelHandler.handleDownstream -> NettyHandler.writeRequested,先执行父类SimpleChannelHandler.writeRequested -> DefaultChannelPipeline.sendDownstream -> OneToOneEncoder.handleDownstream执行doEncode方法。然后执行handler.sent方法。
15 . 这里有多个DefaultChannelHandlerContext,在HeartBeatTask中执行。执行到OneToOneEncoder.doEncode -> NettyCodecAdapter.InternalEncoder.encode -> DubboCountCodec.encode -> ExchangeCodec.encodeRequest进行dubbo协议的编码。另一个则一直调用到DefaultFuture.sent。
provider接受/返回
dubbo 2.7.0版本
1 . FastThreadLocalRunnable.run -> SingleThreadEventExecutor.doStartThread -> NioEventLoop.processSelectedKey -> AbstractNioByteChannel.read -..-> AbstractChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead、invokeChannelRead -> ByteToMessageDecoderchannelRead.channelRead、callDecode、decodeRemovalReentryProtection。最后调用到NettyCodecAdapter.InternalDecoder.decode方法。
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf input, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
ChannelBuffer message = new NettyBackedChannelBuffer(input);
NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler);
Object msg;
int saveReaderIndex;
try {
// decode object.
do {
saveReaderIndex = message.readerIndex();
try {
msg = codec.decode(channel, message);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw e;
}
if (msg == Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT) {
message.readerIndex(saveReaderIndex);
break;
} else {
//is it possible to go here ?
if (saveReaderIndex == message.readerIndex()) {
throw new IOException("Decode without read data.");
}
if (msg != null) {
out.add(msg);
}
}
} while (message.readable());
} finally {
NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ctx.channel());
}
}
2 . 调用DubboCountCodec.decode -> ExchangeCodec.decode方法,根据ChannelBuffer与数据长度创建ChannelBufferInputStream,调用DubboCodec.decodeBody按dubbo协议解析,通过DecodeableRpcInvocation.decode()解析出具体的接口类与参数并放入attachments中,调用CallbackServiceCodec.decodeInvocationArgument()解析出方法请求参数并放入arguments中。
public Object decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) throws IOException {
ObjectInput in = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), serializationType)
.deserialize(channel.getUrl(), input);
String dubboVersion = in.readUTF();
request.setVersion(dubboVersion);
setAttachment(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, dubboVersion);
setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, in.readUTF());
setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, in.readUTF());
setMethodName(in.readUTF());
try {
Object[] args;
Class<?>[] pts;
String desc = in.readUTF();
if (desc.length() == 0) {
pts = DubboCodec.EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY;
args = DubboCodec.EMPTY_OBJECT_ARRAY;
} else {
pts = ReflectUtils.desc2classArray(desc);
args = new Object[pts.length];
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
try {
args[i] = in.readObject(pts[i]);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
log.warn("Decode argument failed: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
setParameterTypes(pts);
Map<String, String> map = (Map<String, String>) in.readObject(Map.class);
if (map != null && map.size() > 0) {
Map<String, String> attachment = getAttachments();
if (attachment == null) {
attachment = new HashMap<String, String>();
}
attachment.putAll(map);
setAttachments(attachment);
}
//decode argument ,may be callback
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
args[i] = decodeInvocationArgument(channel, this, pts, i, args[i]);
}
setArguments(args);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IOException(StringUtils.toString("Read invocation data failed.", e));
} finally {
if (in instanceof Cleanable) {
((Cleanable) in).cleanup();
}
}
return this;
}
3 . 回到DubboCountCodec的decode方法,前面会创建一个MultiMessage。现在将返回的Request对象放入MultiMessage对象,向上返回MultiMessage对象。处理下一个处理器的messageReceived事件。
public Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
int save = buffer.readerIndex();
MultiMessage result = MultiMessage.create();
do {
Object obj = codec.decode(channel, buffer);
if (Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT == obj) {
buffer.readerIndex(save);
break;
} else {
result.addMessage(obj);
logMessageLength(obj, buffer.readerIndex() - save);
save = buffer.readerIndex();
}
} while (true);
if (result.isEmpty()) {
return Codec2.DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT;
}
if (result.size() == 1) {
return result.get(0);
}
return result;
}
4 . 回到NettyCodecAdapter.InternalDecoder的decode方法,将返回放入list中(这个list是在前面的ByteToMessageDecoder.channelRead中定义的CodecOutputList)。向上返回ByteToMessageDecoder后执行fireChannelRead方法。
5 . 一直调到NettyServerHandler.channelRead方法,往后执行到MultiMessageHandler.received -> HeartbeatHandler.received -> AllChannelHandler.received方法,调用cexecutor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.RECEIVED, message))通过线程池启动新的线程处理数据。
6 . 新的处理请求线程ThreadPoolExecutor.Worker.run -> ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker -> ChannelEventRunnable.run -> DecodeHandler.received将message解码 -> HeaderExchangeHandler.received将message封装到request -> HeaderExchangeHandler.handleRequest,执行CompletableFuture
7 . 执行ExchangeHandlerAdapter.reply方法。
public CompletableFuture<Object> reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
if (message instanceof Invocation) {
Invocation inv = (Invocation) message;
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
// need to consider backward-compatibility if it's a callback
if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))) {
String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods");
boolean hasMethod = false;
if (methodsStr == null || !methodsStr.contains(",")) {
hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr);
} else {
String[] methods = methodsStr.split(",");
for (String method : methods) {
if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)) {
hasMethod = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!hasMethod) {
logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName " + inv.getMethodName()
+ " not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored."
+ " please update the api interface. url is:"
+ invoker.getUrl()) + " ,invocation is :" + inv);
return null;
}
}
RpcContext rpcContext = RpcContext.getContext();
boolean supportServerAsync = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(inv.getMethodName(), Constants.ASYNC_KEY, false);
if (supportServerAsync) {
CompletableFuture<Object> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
rpcContext.setAsyncContext(new AsyncContextImpl(future));
}
rpcContext.setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress());
Result result = invoker.invoke(inv);
if (result instanceof AsyncRpcResult) {
return ((AsyncRpcResult) result).getResultFuture().thenApply(r -> (Object) r);
} else {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(result);
}
}
throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: "
+ (message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message))
+ ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress());
}
8 . getInvoker查找提供端请求对应的Invoker,拼接serviceKey,从exporterMap(com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService:20880)中获取DubboExporter,返回exporter.getInvoker()。调用invoker.invoke(inv)方法。通过Invoker-Filter的chain链,依次EchoFilter -> ClassLoaderFilter -> GenericFilter -> ContextFilter -> TraceFilter -> TimeoutFilter -> MonitorFilter -> ExceptionFilter -> InvokerWrapper.invoke -> DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker.invoke -> AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke,调用doInvoke,实际就是调用JavassistProxyFactory里创建的AbstractProxyInvoker的doInvoke方法,里面通过wrapper(proxy)执行wrapper.invokeMethod,反射通过真正的DemoServiceImpl去执行方法,并返回结果。包装成CompletableFuture返回。
9 . 回到HeaderExchangeHandler.received方法获取返回的CompletableFuture
10 . 执行到AbstractChannelHandlerContext.write里,执行ctx.invokeFlush()。继续..调用到NettyServerHandler.write -…> MessageToByteEncoder.write调用encode,在NettyCodecAdapter.encode -> DubboCountCodec.encode -> ExchangeCodec.encode。这里是Response类型,所以就调用encodeResponse(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Response res)方法了。里面类似于encodeRequest,调用encodeResponseData将返回结果写入数据体,写入ChannelBuffer通信链路中。回到MessageToByteEncoder执行ctx.write调用到AbstractChannelHandlerContext.write、invokeWrite。
Consumer接收
dubbo 2.7.0版本
1 . 与服务端接受一样FastThreadLocalRunnable.run -> SingleThreadEventExecutor.doStartThread -> NioEventLoop.processSelectedKey -> AbstractNioByteChannel.read -..-> AbstractChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead、invokeChannelRead -> ByteToMessageDecoderchannelRead.channelRead、callDecode、decodeRemovalReentryProtection。最后调用到NettyCodecAdapter.InternalDecoder.decode方法。里面调用decode进行解码,线程池启动新的线程处理数据等。[参照provider接受/返回 1-5]
/**
按照顺序decoder先执行对服务端传过来的数据进行解码,解析出序列化协议、响应状态、响应id(即请求id)。
把响应body数据读到DecodeableRpcResult对象中,进行解析同时加载处理原始Request数据,
这个Request对象在请求时会被缓存到DefaultFuture中,加载Request的目的是因为Request中Invocation中携带了服务接口的返回值类型信息,
需要根据这个类型把响应解析创建对应类型的对象。此步在DecodeableRpcResult.decode中实现。
*/
protected Object decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header) throws IOException {
byte flag = header[2], proto = (byte) (flag & SERIALIZATION_MASK);
Serialization s = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), proto);
// get request id.
long id = Bytes.bytes2long(header, 4);
if ((flag & FLAG_REQUEST) == 0) {
// decode response.
Response res = new Response(id);
if ((flag & FLAG_EVENT) != 0) {
res.setEvent(Response.HEARTBEAT_EVENT);
}
// get status.
byte status = header[3];
res.setStatus(status);
if (status == Response.OK) {
try {
Object data;
if (res.isHeartbeat()) {
data = decodeHeartbeatData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
} else if (res.isEvent()) {
data = decodeEventData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
} else {
DecodeableRpcResult result;
if (channel.getUrl().getParameter(
Constants.DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD_KEY,
Constants.DEFAULT_DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD)) {
result = new DecodeableRpcResult(channel, res, is,
(Invocation) getRequestData(id), proto);
// 执行DecodeableRpcResult.decode
result.decode();
} else {
result = new DecodeableRpcResult(channel, res,
new UnsafeByteArrayInputStream(readMessageData(is)),
(Invocation) getRequestData(id), proto);
}
data = result;
}
res.setResult(data);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
log.warn("Decode response failed: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
res.setStatus(Response.CLIENT_ERROR);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t));
}
} else {
res.setErrorMessage(deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is).readUTF());
}
return res;
} else {
// decode request.
Request req = new Request(id);
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
req.setTwoWay((flag & FLAG_TWOWAY) != 0);
if ((flag & FLAG_EVENT) != 0) {
req.setEvent(Request.HEARTBEAT_EVENT);
}
try {
Object data;
if (req.isHeartbeat()) {
data = decodeHeartbeatData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
} else if (req.isEvent()) {
data = decodeEventData(channel, deserialize(s, channel.getUrl(), is));
} else {
DecodeableRpcInvocation inv;
if (channel.getUrl().getParameter(
Constants.DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD_KEY,
Constants.DEFAULT_DECODE_IN_IO_THREAD)) {
inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req, is, proto);
inv.decode();
} else {
inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req,
new UnsafeByteArrayInputStream(readMessageData(is)), proto);
}
data = inv;
}
req.setData(data);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
log.warn("Decode request failed: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
// bad request
req.setBroken(true);
req.setData(t);
}
return req;
}
}
2 . DefaultFuture.RemotingInvocationTimeoutScan.run循环判断future,返回后执行DefaultFuture.received钓到received(Channel channel, Response response)方法中。执行future.doReceived唤醒调用者线程并保存response,里面加锁后执行done.signal(),如果有callback执行invokeCallback。
3 . DefaultFuture.get方法里循环阻塞的可以继续进行,通过isDone判断response是否有(避免假唤醒),调用内部returnFromResponse方法,返回res.getResult()。回到DubboInvoker.doInvoke方法。(Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get()终于拿到返回结果或异常。向上返回执行结果并打印。完成一次dubbo服务调用。
4 . 接口调用超时,在DefaultFuture.get方法里判断跳出循环还有个条件就是(System.currentTimeMillis() - start > timeout),这时会向上抛出TimeoutException异常。框架把TimeoutException封装成RpcException抛给应用层。
扩展:
RPC框架(八)dubbo源码分析–dubbo调用过程分析
实现细节
初始化过程细节
解析服务
基于 dubbo.jar 内的 META-INF/spring.handlers 配置,Spring 在遇到 dubbo 名称空间时,会回调 DubboNamespaceHandler。
所有 dubbo 的标签,都统一用 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 进行解析,基于一对一属性映射,将 XML 标签解析为 Bean 对象。
在 ServiceConfig.export() 或 ReferenceConfig.get() 初始化时,将 Bean 对象转换 URL 格式,所有 Bean 属性转成 URL 的参数。
然后将 URL 传给 协议扩展点,基于扩展点的 扩展点自适应机制,根据 URL 的协议头,进行不同协议的服务暴露或引用。
暴露服务
1. 只暴露服务端口:
在没有注册中心,直接暴露提供者的情况下,ServiceConfig 解析出的 URL 的格式为:dubbo://service-host/com.foo.FooService?version=1.0.0。
基于扩展点自适应机制,通过 URL 的 dubbo:// 协议头识别,直接调用 DubboProtocol的 export() 方法,打开服务端口。
2. 向注册中心暴露服务:
在有注册中心,需要注册提供者地址的情况下,ServiceConfig 解析出的 URL 的格式为: registry://registry-host/com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?export=URL.encode("dubbo://service-host/com.foo.FooService?version=1.0.0")。
基于扩展点自适应机制,通过 URL 的 registry:// 协议头识别,就会调用 RegistryProtocol 的 export() 方法,将 export 参数中的提供者 URL,先注册到注册中心。
再重新传给 Protocol 扩展点进行暴露: dubbo://service-host/com.foo.FooService?version=1.0.0,然后基于扩展点自适应机制,通过提供者 URL 的 dubbo:// 协议头识别,就会调用 DubboProtocol 的 export() 方法,打开服务端口。
引用服务
1. 直连引用服务:
在没有注册中心,直连提供者的情况下,ReferenceConfig 解析出的 URL 的格式为:dubbo://service-host/com.foo.FooService?version=1.0.0。
基于扩展点自适应机制,通过 URL 的 dubbo:// 协议头识别,直接调用 DubboProtocol 的 refer() 方法,返回提供者引用。
2. 从注册中心发现引用服务:
在有注册中心,通过注册中心发现提供者地址的情况下,ReferenceConfig 解析出的 URL 的格式为:registry://registry-host/com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?refer=URL.encode("consumer://consumer-host/com.foo.FooService?version=1.0.0")。
基于扩展点自适应机制,通过 URL 的 registry:// 协议头识别,就会调用 RegistryProtocol 的 refer() 方法,基于 refer 参数中的条件,查询提供者 URL,如: dubbo://service-host/com.foo.FooService?version=1.0.0。
基于扩展点自适应机制,通过提供者 URL 的 dubbo:// 协议头识别,就会调用 DubboProtocol 的 refer() 方法,得到提供者引用。
然后 RegistryProtocol 将多个提供者引用,通过 Cluster 扩展点,伪装成单个提供者引用返回。
拦截服务
基于扩展点自适应机制,所有的 Protocol 扩展点都会自动套上 Wrapper 类。
基于 ProtocolFilterWrapper 类,将所有 Filter 组装成链,在链的最后一节调用真实的引用。
基于 ProtocolListenerWrapper 类,将所有 InvokerListener 和 ExporterListener 组装集合,在暴露和引用前后,进行回调。
包括监控在内,所有附加功能,全部通过 Filter 拦截实现。
远程调用细节
服务提供者暴露一个服务的详细过程
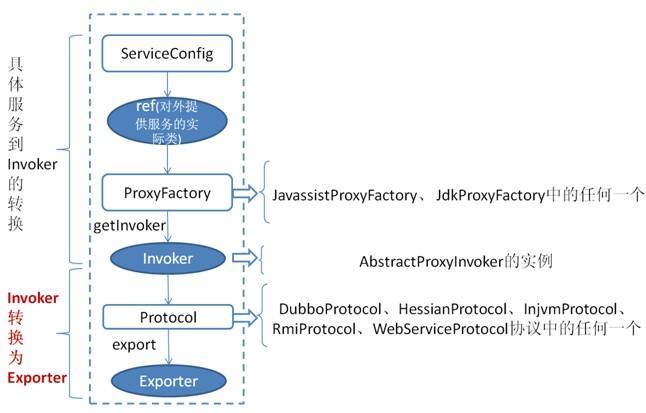
上图是服务提供者暴露服务的主过程:
首先 ServiceConfig 类拿到对外提供服务的实际类 ref(如:HelloWorldImpl),然后通过 ProxyFactory 类的 getInvoker 方法使用 ref 生成一个 AbstractProxyInvoker 实例,到这一步就完成具体服务到 Invoker 的转化。接下来就是 Invoker 转换到 Exporter 的过程。
Dubbo 处理服务暴露的关键就在 Invoker 转换到 Exporter 的过程,上图中的红色部分。下面我们以 Dubbo 和 RMI 这两种典型协议的实现来进行说明:
Dubbo 的实现
Dubbo 协议的 Invoker 转为 Exporter 发生在 DubboProtocol 类的 export 方法,它主要是打开 socket 侦听服务,并接收客户端发来的各种请求,通讯细节由 Dubbo 自己实现。
RMI 的实现
RMI 协议的 Invoker 转为 Exporter 发生在 RmiProtocol类的 export 方法,它通过 Spring 或 Dubbo 或 JDK 来实现 RMI 服务,通讯细节这一块由 JDK 底层来实现,这就省了不少工作量。
服务消费者消费一个服务的详细过程
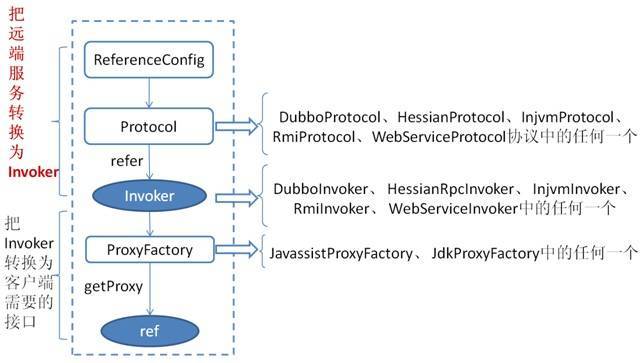
上图是服务消费的主过程:
首先 ReferenceConfig 类的 init 方法调用 Protocol 的 refer 方法生成 Invoker 实例(如上图中的红色部分),这是服务消费的关键。接下来把 Invoker 转换为客户端需要的接口(如:HelloWorld)。
关于每种协议如 RMI/Dubbo/Web service 等它们在调用 refer 方法生成 Invoker 实例的细节和上一章节所描述的类似。
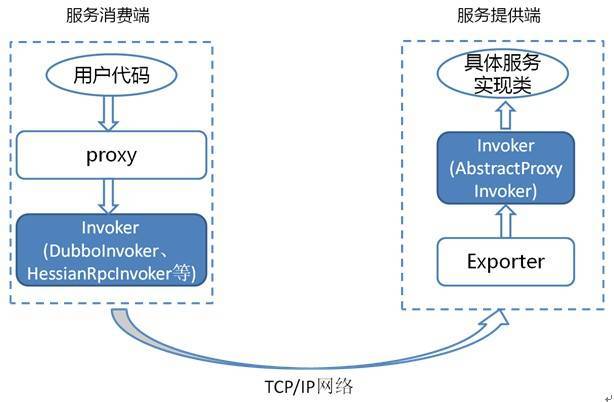
远程通讯细节
协议头约定
线程派发模型
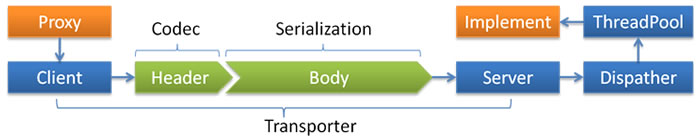
- Dispather: all, direct, message, execution, connection
- ThreadPool: fixed, cached