SpringBoot(一) 启动与自动配置
SpringBoot(二) starter与servlet容器
SpringBoot(三) Environment
SpringBoot(四) 集成apollo遇到的事儿
SpringBoot(五) 健康检查(上)
SpringBoot(六) 健康检查(下)
Environment
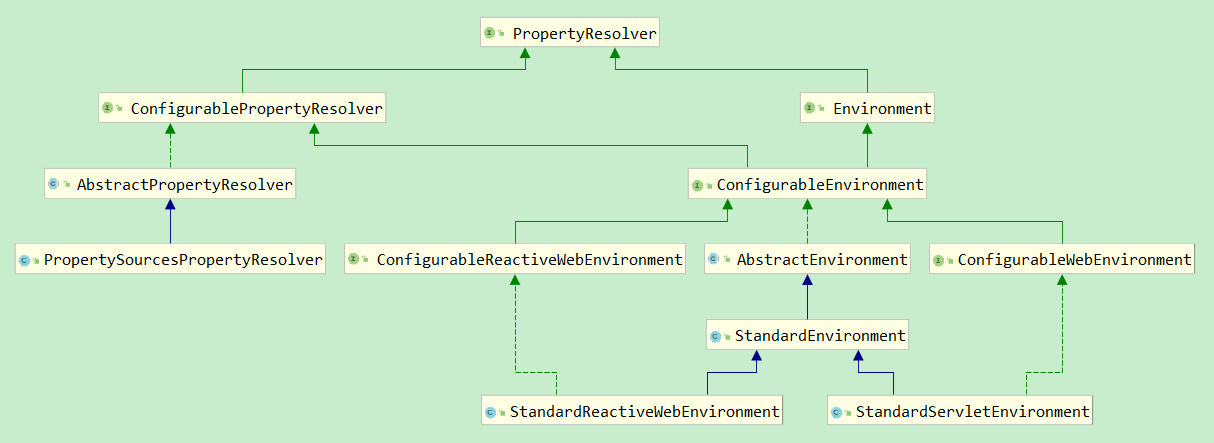 Environment接口是暴露出来当前运行环境的公开接口,从接口方法可以看出,主要实现功能分为两个关键部分,Properties属性和Profile环境配置文件
Environment接口是暴露出来当前运行环境的公开接口,从接口方法可以看出,主要实现功能分为两个关键部分,Properties属性和Profile环境配置文件
- PropertyResolver:提供属性访问功能
- ConfigurablePropertyResolver:继承自PropertyResolver,额外提供属性类型转换(基于org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService)功能
- Environment:继承自PropertyResolver,额外提供访问和判断profiles的功能
- ConfigurableEnvironment:继承自ConfigurablePropertyResolver和Environment,并且提供设置激活的profile和默认的profile的功能
- ConfigurableWebEnvironment:继承自ConfigurableEnvironment,并且提供配置Servlet上下文和Servlet参数的功能
- AbstractEnvironment:实现了ConfigurableEnvironment接口,默认属性和存储容器的定义,并且实现了ConfigurableEnvironment中的方法,并且为子类预留可覆盖了扩展方法
- StandardEnvironment:继承自AbstractEnvironment,非Servlet(Web)环境下的标准Environment实现
- StandardServletEnvironment:继承自StandardEnvironment,Servlet(Web)环境下的标准Environment实现
- Reactive相关接口
Environment的静态属性和存储容器都是在AbstractEnvironment中定义的:
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
// Environment的存储容器就是org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource的子类集合
public class MutablePropertySources implements PropertySources {
private final List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// ...
}
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {
protected final String name;
protected final T source;
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return (this == other || (other instanceof PropertySource &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.name, ((PropertySource<?>) other).name)));
}
public int hashCode() {
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.name);
}
//...
}
从重写的equals和hashCode可以看出,一个PropertySource实例绑定到一个唯一的name,这个name有点像HashMap里面的key,这些说明只和name属性有关。PropertySource的最常用子类是:
1、MapPropertySource:继承自EnumerablePropertySource,source指定为Map实例的PropertySource实现
2、PropertiesPropertySource:继承自MapPropertySource,source指定为Map实例的PropertySource实现,内部的Map实例由Properties实例转换而来
3、ResourcePropertySource:继承自PropertiesPropertySource,source指定为通过Resource实例转化为Properties再转换为Map实例
4、StubPropertySource:PropertySource的一个内部类,source设置为null,实际上就是空实现
5、ComparisonPropertySource:继承自StubPropertySource,所有属性访问方法强制抛出异常,作用就是一个不可访问属性的空实现
再回过头看MutablePropertySources,list创建的是一个CopyOnWriteArrayList,这是配置属性的底层存储数据结构,MutablePropertySources是PropertySources的一个子类,也提供了get、addFirst、addLast、addBefore、addAfter、remove、replace等便捷方法
然后来看AbstractEnvironment中的另一个属性,Environment属性的访问都是委托到PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的:
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver是ConfigurablePropertyResolver的实现,默认的profile就是字符串default
加载配置
在SpringApplication的run方法中,会进行Environment加载:
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 1. Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 启动参数绑定到ConfigurableEnvironment中
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 2. 发布ConfigurableEnvironment准备完毕事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 绑定ConfigurableEnvironment到当前的SpringApplication实例中
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
//
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 绑定ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource到ConfigurableEnvironment中,其name为configurationProperties;实例是SpringConfigurationPropertySources,内部是ConfigurableEnvironment中的MutablePropertySources
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
1、看一下getOrCreateEnvironment方法时怎么创建ConfigurableEnvironment的:
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
// SpringMVC项目
case SERVLET:
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
2、发布ConfigurableEnvironment准备完毕事件,这里用到了同步的EventBus,事件的监听者是ConfigFileApplicationListener,具体处理逻辑是onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent方法:
// EventPublishingRunListener
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
// SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
});
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
// ConfigFileApplicationListener
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
// 遍历所有的EnvironmentPostProcessor对Environment实例进行处理
/**
0 = {SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor@2303}
1 = {SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor@2304}
2 = {CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor@2305}
3 = {ConfigFileApplicationListener@2235}
4 = {SpringBootTestRandomPortEnvironmentPostProcessor@2306}
**/
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> loadPostProcessors() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(EnvironmentPostProcessor.class, getClass().getClassLoader());
}
大部分的逻辑处理在ConfigFileApplicationListener中,见其postProcessEnvironment方法:
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
// 主要的配置环境加载逻辑在内部类Loader,Loader会匹配多个路径下的文件把属性加载到ConfigurableEnvironment中,加载器主要是PropertySourceLoader的实例
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
可见其内部类Loader:
public void load() {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (profile != null && !profile.isDefaultProfile()) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
resetEnvironmentProfiles(this.processedProfiles);
// 加载配置
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
addLoadedPropertySources();
}
private void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
/**
0 = "file:./config/"
1 = "file:./"
2 = "classpath:/config/"
3 = "classpath:/"
**/
getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> {
boolean isFolder = location.endsWith("/");
Set<String> names = isFolder ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;
// name = application
names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));
});
}
比如用到application-${profile}.yaml文件做应用主配置文件,使用的是YamlPropertySourceLoader,这个时候activeProfiles也会被设置到ConfigurableEnvironment中。加载完毕之后,ConfigurableEnvironment中基本包含了所有需要加载的属性,所有属性都是key-value形式存储的(activeProfiles这时被写入ConfigurableEnvironment)
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory,
DocumentConsumer consumer) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, location)) {
load(loader, location, profile, filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile), consumer);
return;
}
}
}
Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>();
/**
0 = {PropertiesPropertySourceLoader@2854}
1 = {YamlPropertySourceLoader@2855}
**/
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
/**
0 = "properties"
1 = "xml"
**/
for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) {
if (processed.add(fileExtension)) {
loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory,
consumer);
}
}
}
}
部分配置demo,集成maven和Spring boot的profile:
application.yml:
spring:
profiles:
active: @profileActive@
或者spring,applicationContext.xml:
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:${env}/**/*.properties" />
或者使用maven-assembly-plugin,assembly.xml:
<assembly>
...
<fileSet>
<directory>src/main/resources/${env}</directory>
<outputDirectory>conf</outputDirectory>
<fileMode>0644</fileMode>
</fileSet>
...
</assembly>
获取属性
AbstractEnvironment中定义的属性ConfigurablePropertyResolver,即PropertySourcesPropertyResolver实例作为访问属性的委托,构造方法里设置了一个PropertySources实例。看下它的getProperty方法:
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
// 遍历所有的PropertySource
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" +
propertySource.getName() + "'");
}
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
// 选用第一个不为null的匹配key的属性值,即如果出现多个PropertySource中存在同名的key,返回的是第一个PropertySource对应key的不为null属性值的处理结果
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
// 处理属性占位符,如${server.port},底层委托到PropertyPlaceholderHelper完成
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
// 如果需要的话,进行一次类型转换,底层委托到DefaultConversionService完成
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source");
}
return null;
}
所以总结而言,对于Spring环境属性的管理:从文件中读取数据转化为key-value结构,key-value结构存放在一个PropertySource实例中,然后得到的多个PropertySource实例存放在一个CopyOnWriteArrayList中,属性访问的时候总是遍历CopyOnWriteArrayList中的PropertySource进行匹配,再涉及一些占位符的解析和参数类型的转换
扩展:
Spring 学习记录2 Environment
Spring Environment的加载